In terms of the stock market, systematic risk refers to the fact that
A) some stocks have higher returns than others.
B) some stocks' returns have a higher variance than others.
C) all stock prices are correlated with the health of the economy.
D) most stock prices are perfectly negatively correlated.
C
You might also like to view...
Having a comparative advantage means a nation can
A) benefit from trade. B) produce at a higher opportunity cost. C) produce more of the good. D) produce without incurring an opportunity cost. E) produce the good at a point beyond its PPF.
The Sherman Act of 1890 and the Clayton Act of 1914 were Antitrust Acts whose purposes included all of the following except
(a) The maintenance of a competitive economy (b) The prevention of monopolies, combinations and other conspiracies in restraint of trade (c) The prevention of price discrimination that reduces competition (d) The prevention of labor union activity that reduces competition in the labor market
Pete is a non-union employee at The Electric Co The majority of the employees at The Electric Co are unionized. The union at The Electric Co has negotiated very good benefits. Even though he is not a union member and he does not have to pay union dues, Pete receives all the benefits that the union has negotiated. Pete's behavior is an example of
a. rivalry. b. a barrier to entry. c. free riding. d. Taft-Hartley opposition.
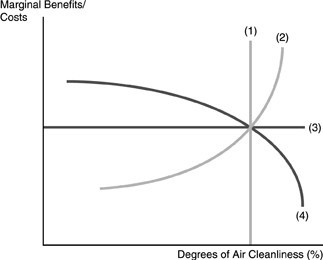 Refer to the above figure. Suppose the marginal benefit and the marginal cost curves of pollution abatement are normally shaped. Technological change that made it easier to produce in a "cleaner" fashion would cause
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the marginal benefit and the marginal cost curves of pollution abatement are normally shaped. Technological change that made it easier to produce in a "cleaner" fashion would cause
A. curve (1) to shift out, increasing the optimal amount of pollution abatement. B. curve (3) to shift up, raising the marginal benefits and costs and reducing the amount of pollution abatement. C. curve (4) to shift out, increasing the optimal amount of pollution abatement. D. curve (2) to shift out, increasing the optimal amount of pollution abatement.