What are the economic effects of imposition of a new occupational license or examination on a labor market?
What will be an ideal response?
The primary effect of occupational licensing or testing is to restrict entry into a profession. The imposition of a new licensing requirement has the effect of reducing the supply of workers who are “qualified” for the job. Given a stable demand for an occupation, the reduction in supply will tend to increase the equilibrium wage in the labor market.
The typical reason that is given for licensing requirements is to make certain that people are qualified for an occupation. However, unnecessarily stringent requirements or difficult tests can serve to restrict entry without significantly increasing worker quality. In these instances, the economic effect of the new rule or regulation serves to increase wages of workers above the competitive wage in that industry.
You might also like to view...
When the aggregate demand curve shifts,
A) the inflation rate does not change. B) there is a movement along the short-run Phillips curve. C) there is a change in potential GDP. D) there is a change in the natural unemployment rate. E) the short-run Phillips curve shifts.
Immediately after the Federal Reserve buys government securities,
A) bank excess reserves rise. B) bank excess reserves fall. C) bank capital rises. D) bank capital falls.
Refer to the below graph, where TP = total product and L = labor input. The marginal product of labor (MP):
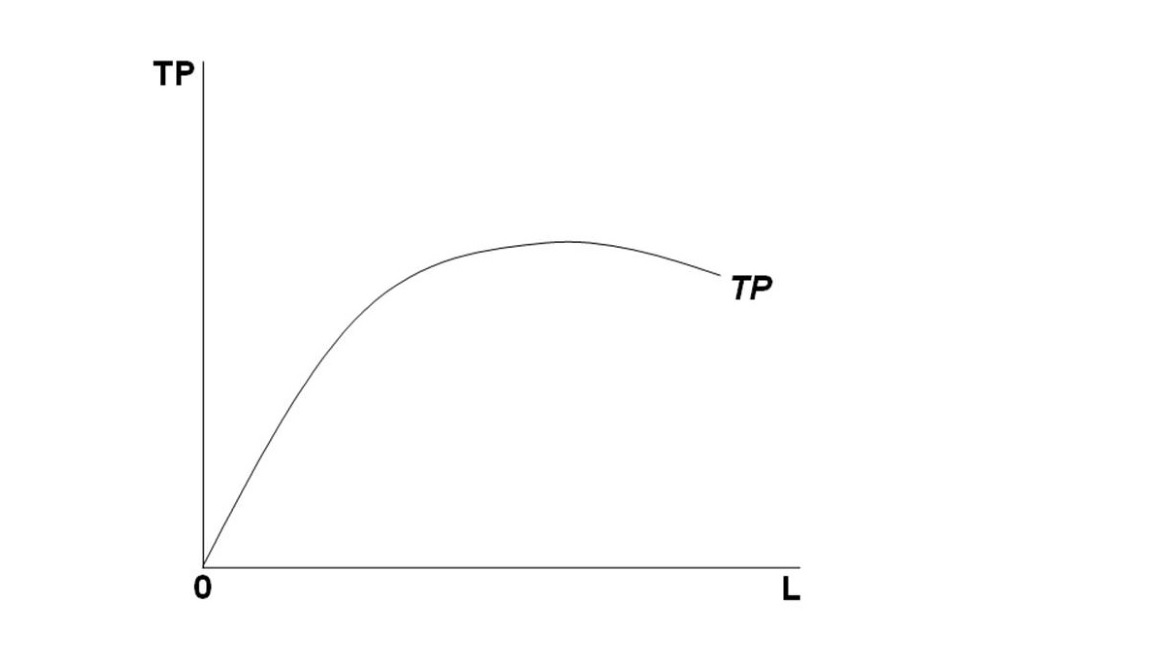
A. Is constant at all levels of L
B. Increases at an increasing rate as L increases
C. Decreases as the labor input L increases
D. Increases at a decreasing rate as L increases
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 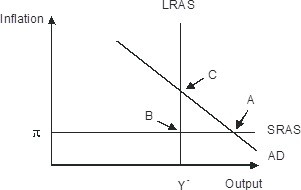
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward