Many companies have to monitor some of their financial statement ratios, such as the current ratio, due to debt covenants. Selected transactions are provided below for a company that uses a perpetual inventory system; sells its merchandise at a selling price that exceeds cost; and had a current ratio of 1.85 to 1 before the event occurred.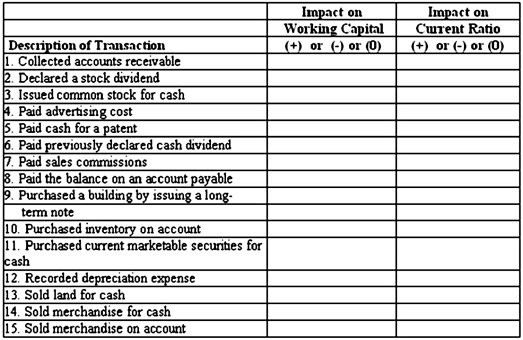 Required:In the above table, indicate whether each transaction would increase (+), decrease (?), or not affect (0) the company's working capital and the current ratio.
Required:In the above table, indicate whether each transaction would increase (+), decrease (?), or not affect (0) the company's working capital and the current ratio.
What will be an ideal response?
Working capital = Current assets ? Current liabilities
Current ratio = Current assets ÷ Current liabilities
Impact of each transaction on these components:
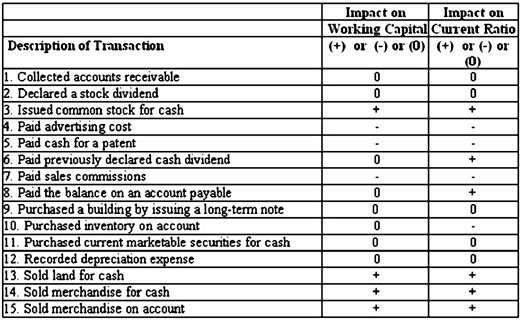
1. No change in current assets (since increase in cash equals decrease in accounts receivable) and no change in current liabilities
2. No change in current assets or current liabilities
3. Increase in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
4. Decrease in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
5. Decrease in current assets (cash) but no change in current liabilities
6. Decrease in current assets (cash) and decrease in current liabilities (dividends payable).
To determine the impact on the current ratio, assume that the current ratio of 1.85 to 1 meant that current assets were $185,000 and current liabilities were $100,000 and the dividend payment was for $10,000. The new current ratio would then equal ($185,000 ? $10,000) ÷ ($100,000 ? $10,000) = $175,000 ÷ $90,000 = 1.94 (which is an increase from 1.85 to 1).
8. Decrease in current assets (cash) and decrease in current liabilities (accounts payable)
To determine the impact on the current ratio, assume that the current ratio of 1.85 to 1 meant that current assets were $185,000 and current liabilities were $100,000 and the payment on account was for $10,000. The new current ratio would then equal ($185,000 ? $10,000) ÷ ($100,000 ? $10,000) = $175,000 ÷ $90,000 = 1.94 (which is an increase from 1.85 to 1).
9. No change in current assets or current liabilities
10. No change in current assets (inventory) and increase in current liabilities (accounts payable)
11. No change in current assets (since increase in cash equals decrease in current marketable securities) and no change in current liabilities
12. No change in current assets or current liabilities
13. Increase in current assets (cash) and no change in current liabilities
14. Increase in current assets (since increase in cash exceeds decrease in inventory) and no change in current liabilities
15. Increase in current assets (since increase in account receivable exceeds decrease in inventory) and no change in current liabilities
You might also like to view...
Best Buy is a category specialist for the electronics industry. This means the stores
A. have excellent after-sales customer service. B. avoid a self-service approach. C. offer a narrow but deep assortment of merchandise. D. sell only their own private-label brands. E. offer their customers narrow breadth and depth of merchandise.
With respect to standardized information, CGM stands for:
A) consumer-granted marketing B) consumer-generated media C) customer-given media D) customers' generic marketing E) connector-generated marketing
Retaliatory trade restrictions are not made for dumping because price competition is protected by the WTO.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
__________is the element in the promotional mix that evaluates people's attitudes, identifies issues that may elicit their concern, and executes programs to gain their understanding and acceptance
Fill in the blanks with correct word.