Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 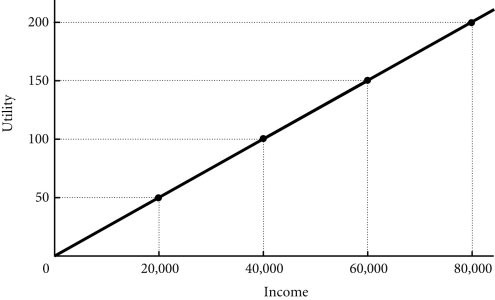 Figure 17.2 Refer to Figure 17.2. Sam has two job offers when he graduates from college. Sam views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $60,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $30,000 plus a possible bonus of $60,000. Sam believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. If Sam takes the offer that maximizes his expected utility and is risk-neutral, which job offer will he choose?
Figure 17.2 Refer to Figure 17.2. Sam has two job offers when he graduates from college. Sam views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $60,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $30,000 plus a possible bonus of $60,000. Sam believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. If Sam takes the offer that maximizes his expected utility and is risk-neutral, which job offer will he choose?
A. Sam will take the first offer.
B. Sam will take the second offer.
C. Sam is indifferent between the offers-both yield the same expected utility.
D. Indeterminate from the given information.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If Second National Bank has more rate-sensitive liabilities then rate-sensitive assets, it can reduce interest rate risk with a swap that requires Second National to
A) pay fixed rate while receiving floating rate. B) receive fixed rate while paying floating rate. C) both receive and pay fixed rate. D) both receive and pay floating rate.
A monopolist faces the inverse demand curve P = 60 - Q. It has variable costs of Q2 so that its marginal costs are 2Q, and it has fixed costs of 30
If a governmental agency imposes an $8 per unit specific tax on output, the deadweight loss from both the monopoly and the tax is A) $37.50. B) $73.00 C) $526.50. D) $562.50.
Which of the following is not a step involved in cost-benefit analysis?
a. Conversion of the costs and benefits to dollar terms. b. Enumeration of the costs and benefits. c. Enumeration of the special interests. d. Enumeration of the options.
A firm gets less efficient as it gets bigger, if it is experiencing:
a. economies of scale. b. constant returns to scale. c. increasing returns to factors. d. diseconomies of scale. e. a period of post war recovery.