Assume that banks become more conservative in their lending policies and start holding some excess reserves. Compared to a situation in which banks are not holding excess reserves, the size of the money supply will be
A. larger.
B. the same.
C. smaller.
D. zero.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If the shares of stock that Doug owns go up in value from $10,000 to $15,000, then Doug's wealth:
A. does not change. B. increases by $15,000. C. decreases by $5,000. D. increases by $5,000.
Which of the following correctly describes a way in which deficit spending can impose a burden on future generations?
I. Failure to allocate deficit spending to uses that boost future real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) will require taxing future generations at a higher rate to repay the resulting higher public debt. II. Government deficits that lead to higher employment and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in the future will generate increased income taxes for future governments, which will respond by spending the higher tax revenues, creating higher future government budget deficits. III. Other things being equal, deficit spending fuels increased consumption of goods and services by the current generation that crowds out capital investment, thereby leaving future generations with a smaller stock of capital than otherwise would have existed. A) I only B) II only C) I and III only D) II and III only
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, explain and demonstrate graphically the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in the money supply
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the graph below for a monopolist in short-run equilibrium. This monopolist will charge a price:
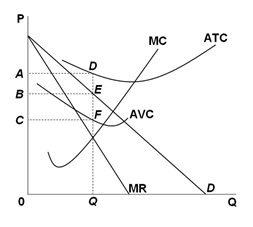
A. 0A
B. 0B
C. 0C
D. Not labeled on the graph