Stagflation refers to
a. inflation that rises and falls from year to year.
b. increasing output above full-employment levels and thus fueling inflation.
c. sluggish production combined with inflation.
d. staggered decreases in the money supply designed to lower inflation.
c. sluggish production combined with inflation.
You might also like to view...
For a firm in the long-run, an increase in the market wage rate will cause it to reduce the employment of labor. With fewer workers, the firm's marginal revenue product for capital
a. shifts downward leading the firm to use less capital. b. shifts upward leading the firm to use more capital. c. twists so that is becomes more elastic d. is not affected.
The U.S. government has frequently used a "command-and-control" approach in dealing with pollution. Which of the following describes this approach?
A) The government imposes quantitative limits on the amount of pollution firms are allowed to generate. B) The government distributes information to consumers and producers on how to reduce pollution. C) The government uses subsidies to encourage firms to use new technology that reduces pollution. D) The government uses taxes in order to internalize the externalities caused by pollution.
According to the above table, at a price of $2 per unit, which of the following would exist?
A) a shortage of 800 units B) a surplus of 800 units C) a shortage of 200 units D) a shortage of 400 units
Refer to the given data. Suppose the Fed wants to increase the money supply by $400 billion to drive down interest rates and stimulate the economy. Assuming that the money multiplier is operating to full effect, to accomplish the desired increase, the Fed could:
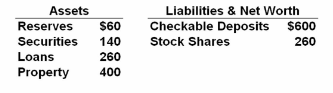
Answer the question on the basis of the following consolidated balance sheet of the
commercial banking system. Assume that the reserve requirement is 10 percent. All figures
are in billions and each question should be answered independently of changes specified in
any preceding ones.
A. sell $20 billion of U.S. securities to the banks.
B. buy $20 billion of U.S. securities from the banks.
C. sell $40 billion of U.S. securities to the banks.
D. buy $40 billion of U.S. securities from the banks.