What is microevolution?
A. an individual organism changing its behavior to respond to its environment
B. the major events in the origin of life on earth
C. the evolution of microorganisms over the last 3 billion years
D. a change at the genetic level in a small population that can occur in a single generation
E. All of the above are correct.
Ans: D. a change at the genetic level in a small population that can occur in a single generation
You might also like to view...
An experiment was done to determine the decimal reduction time of a specific population of organisms at 80oC. The data is indicated by an arrow on the graph. Which labeled line represents the likely results if the experiment was repeated at the same temperature, but starting with a larger number of organisms?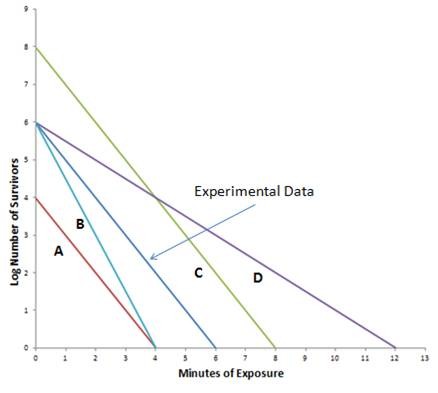
A. Line D B. Line C C. Line A D. Line B
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a signaling molecule that functions in which of the following types of cell signaling?
A. juxtacrine B. paracrine C. autocrine D. endocrine E. All of these choices are correct.
Sidney Brenner found bacteriophage T4 point mutants in which a protein was prematurely terminated. The premature termination point of the protein was different in different mutants
When he determined where the protein synthesis terminated for each mutant, in every case the next amino acid of the protein would have been a glutamine, lysine, glutamic acid, tyrosine, or serine. What is the unique similarity of these amino acids or their codons that would play a role in the premature termination of translation in the mutant protein gene? A. Each of the amino acids has an R-group containing an amine, hydroxyl, or carboxyl group. B. Each of the codons for these amino acids contains either U or G. C. Each of the codons for these amino acids could be changed to UAG with a single nucleotide mutation. D. Each of the amino acids is polar and charged.
Genes are found in the same order for large stretches of the X chromosome in the rat and mouse genomes, indicating
A. conservation of neoteny. B. conservation of synteny. C. occurrence of aneuploidy. D. formation of pseudogenes.