What is primarily responsible for the development of a resting membrane potential?
a. More diffusion and active transport of cations out of the cell than into the cell
b. Pumping 2 K+ ions out of the cell for every three Na+ ions pumped into the cell
c. More K+ ions diffusing into the cell than there are Na+ ions diffusing out of the cell
d. More anions diffusing into the cell than are diffusing out of the cell
e. None of the above are primarily responsible.
C
You might also like to view...
What is the purpose of motor nerve varicosities as they relate to smooth muscle?
A. They link the thin filaments to the inside of the sarcolemma in smooth muscle. B. They reabsorb the decomposition products of acetylcholine after acetylcholinesterase breaks it down. C. They enable each cardiac myocyte to directly stimulate its neighbors. D. They release neurotransmitter onto smooth muscle cells. E. They prevent single-unit smooth muscle cells from pulling apart.
Axons of the corticobulbar tract terminate in the
A) sensory neurons. B) somatic motor neurons in the spinal cord. C) autonomic motor neurons in the spinal cord. D) motor nuclei of cranial nerves. E) nuclei in the thalamus.
Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
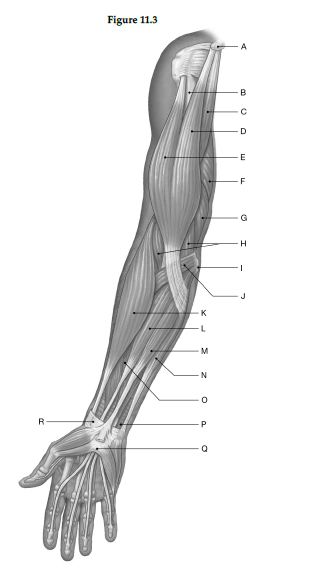
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
The bony portion of the nasal septum is formed by the
a. perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and vomer. b. perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone only. c. nasal bones and perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. d. vomer and sphenoid bones.