How do consumers react to a tax on an item with few or no substitutes?
a. They stop consuming the product.
b. They consume a bit less.
c. They consume considerably less.
d. They consume a bit more.
b. They consume a bit less.
You might also like to view...
What is not true for a system of financial penalties for polluters?
A. Firms may be fined for pollution. B. Firms might have to pay a tax for each unit of pollution created. C. Firms would be encouraged to pollute less. D. Firms are always guaranteed the permit to pollute.
Suppose the exchange rate for 1 euro is $1.40. Purchasing power parity exists if a fast-food meal in the United States costs $5 and in Paris, that same fast-food meal costs:
a) 2.59 euros. b) 3.43 euros. c) 3.57 euros. d) 7 euros.
Use the following graph of the demand for noodles to answer the question below.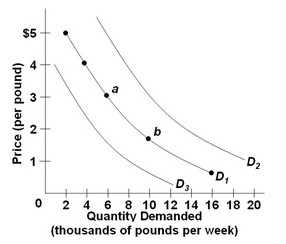 Refer to the three demand curves for noodles and assume noodles are an inferior good. Which of the following would shift the demand for noodles from D1 to D2?
Refer to the three demand curves for noodles and assume noodles are an inferior good. Which of the following would shift the demand for noodles from D1 to D2?
A. an increase in consumer incomes B. a decrease in consumer incomes C. a decrease in the price of noodles D. an increase in the price of noodles
A risk-averse individual would:
A. prefer a risky prospect with an expected value of $5 to a certain amount of $5. B. prefer $5 with certainty to a risky prospect with the expected value of $50. C. be indifferent between a risky prospect with an expect value of $5 and a certain amount of $5. D. prefer $5 with certainty to a risky prospect with the expected value of $5.