How might unemployment insurance increase the efficiency of labor markets and the economy? How might it reduce the efficiency of labor markets and the economy?
What will be an ideal response?
Unemployment insurance is a government program that allows workers to receive benefits for a period of time after losing their jobs. The job search associated with frictional unemployment allows workers to find jobs that pay the most and to find jobs where they can be the most productive. When workers are more productive, they have a higher marginal product of labor, which should lead to higher real wages and more employment. With unemployment insurance, those workers who are frictionally unemployed are under less pressure to accept the first job offered and can better afford to search for jobs that match their skills and pay the most. It is possible that if unemployment insurance is offered for too long a period of time, workers lose the incentive to actively search for a new job, which would reduce economic efficiency.
You might also like to view...
Private goods and club goods have in common that they are excludable, but are different in that private goods are rival while club goods are not rival in consumption
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The ability of banks to get insurance from ______________ encourages banks to take on a little bit _________ risk than they would in the absence of deposit insurance
A) the FDIC; less B) Fannie Mae (FNMA); more C) the FDIC; more D) Fannie Mae (FNMA); less
Refer to the graph shown.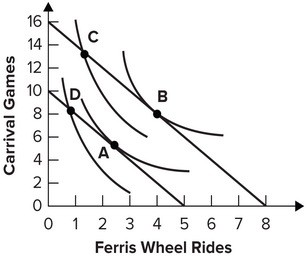 A consumer would be expected to change consumption from point A to point B in response to a(n):
A consumer would be expected to change consumption from point A to point B in response to a(n):
A. increase in income. B. decrease in income. C. decrease in the price of Ferris wheel rides. D. decrease in the price of carnival games.
Suppose that a consumer is currently at an optimum when consuming goods A and B. Which of the following must be TRUE?
A) The total utility from A is equal to the total utility from B. B) The price of A is equal to the price of B. C) The marginal utility of A is equal to the marginal utility of B. D) The marginal utility to price ratio of A is equal to the marginal utility to price ratio of B.