The legality of ________ under Section 1 of the Sherman Act is examined by using the rule of reason.
A. division of markets
B. nonprice vertical restraints of trade
C. price fixing
D. market sharing
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Aisha has been asked to organize a team of managers to make decisions regarding some key issues within her company. She has been given a very tight timeline and is concerned about the impacts of cognitive bias and groupthink. Aisha is familiar with techniques such as devil's advocacy and dialectical inquiry and knows they can help combat these issues, but she feels they would take too much time. What advice would you give Aisha about choosing group members?
What will be an ideal response?
Data Processing, Inc is a service firm that performs word processing functions for law firms, corporations and government agencies. Their facilities consist of 120 office units with a word processor in each unit. Their facilities were formerly a shoe
manufacturing plant, and all of the office units are located in one large room. Over the past 14 months, 7 of the 120 word processors have been diagnosed with breast cancer. In six of the seven cases diagnosed, there is no family history of breast cancer. Jane Quinn, the owner and CEO of data processing, has seen a cluster study that links employment as a word processor to a higher rate of breast cancer. Ms. Quinn does not disclose the study to her employees and takes no further action. Discuss the ethical issues.
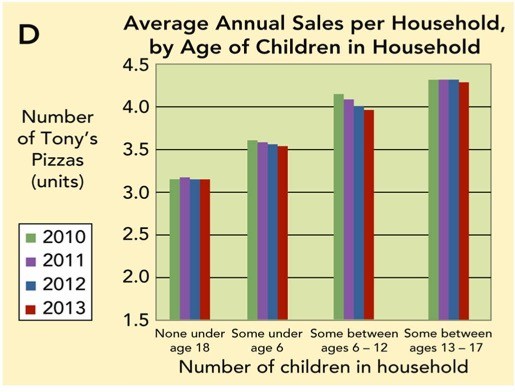 Figure 7-6D: Average Annual Sales per Household of Tony's Pizza, by Age of Children in HouseholdFigure 7-6D above shows average annual unit sales per household, by age of children in household for Tony's Pizza. Analyze this chart. What findings would you present to a supervisor?
Figure 7-6D: Average Annual Sales per Household of Tony's Pizza, by Age of Children in HouseholdFigure 7-6D above shows average annual unit sales per household, by age of children in household for Tony's Pizza. Analyze this chart. What findings would you present to a supervisor?
What will be an ideal response?
Gertie has a NSTCL of $9,000 and a NLTCG of $5,500 during the current taxable year. After gains and losses are offset, Gertie reports
A.
| An offset against ordinary income | Loss carryforward |
| $3,000 | $0 |
B.
| An offset against ordinary income | Loss carryforward |
| $3,000 | $6,000 |
C.
| An offset against ordinary income | Loss carryforward |
| $3,000 | $500 |
D.
| An offset against ordinary income | Loss carryforward |
| $3,500 | $0 |