Along an indifference curve
A. the price ratio is constant.
B. the ratio of the marginal utilities is constant.
C. the MRS is constant.
D. all of the above
E. none of the above
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Fuji and Kodak produce identical film. The market demand for film is given by P = 8 - Q, where P is the price (in dollars per roll of film) and Q is the quantity (in hundreds of rolls). Each firm has the option of producing 150, 200, or 300 rolls of film at a constant marginal cost of $2 per roll with no fixed costs. The firms' possible profits for various outcomes are summarized in the accompanying table.
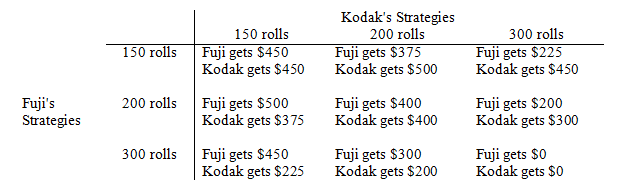
(i) If the two firms behave competitively, what will be the outcome of this game? Is this outcome Pareto optimal for the firms?
(ii) If the two firms merge and form a monopoly, what will be the outcome of this game? Is this outcome Pareto optimal for the firms?
(iii) What is the Nash equilibrium for this game? Is it Pareto optimal for the firms? How does it compare with the competitive and monopoly outcomes?
(iv) Suppose this game is played sequentially, with Fuji as the first player. What will be the Stackelberg equilibrium? Is it Pareto optimal?
Which of the following statements is TRUE about the role of gifts given to U.S. citizens from foreign residents?
A) Gifts are not included in the balance of payments because of the nature of the gift. B) Gifts are only included in the balance of payments if the gift is given to a government official. C) Gifts are included in the balance of payments. D) Gifts given to U.S. citizens are not included in the balance of payments but gifts given to foreigners are included.
Last year an economy produced 3400 hurleys, 3000 footballs and 2000 rugby balls. The price of hurleys was €30, the price of footballs was €20 and the price of rugby balls was €25. Nominal GDP was:
(a) €212,000. (b) €660,000. (c) €420,250. (d) Cannot be computed.
A delivery company lowers its automobile insurance costs as it increases in size because as the size of the fleet of delivery trucks increases, the premium per driver decreases substantially. This is an example of
A. constant returns to scale. B. diseconomies of scale. C. diminishing marginal returns. D. economies of scale.