In a long-run equilibrium, the marginal firm has
a. price equal to minimum marginal cost.
b. total revenue equal to total cost.
c. accounting profit equal to zero.
d. All of the above are correct.
b
You might also like to view...
When policy makers choose between tax policy and spending policy to affect the level of aggregate demand, they tend to choose on the basis of
a. how large a public sector they want. b. how much they want to change aggregate demand. c. how much they want to change aggregate supply. d. which has the larger multiplier.
Suppose an economy produces only eggs and ham. In 2009, 100 dozen eggs are sold at $3 per dozen and 50 pounds of ham sold at $4 per pound. In 2010, the base year, eggs sold at $1.50 per dozen and ham sold at $5 per pound. For 2009,
a. nominal GDP is $400, real GDP is $500, and the GDP deflator is 80. b. nominal GDP is $400, real GDP is $500, and the GDP deflator is 125. c. nominal GDP is $500, real GDP is $400, and the GDP deflator is 80. d. nominal GDP is $500, real GDP is $400, and the GDP deflator is 125.
Refer to the graph shown.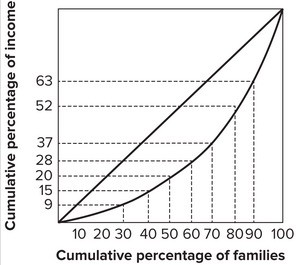 The poorest 30 percent of the families earn:
The poorest 30 percent of the families earn:
A. 9 percent of the income. B. 15 percent of the income. C. 2 percent of the income. D. 5 percent of the income.
A classical IS-LM model of the world economy can be used to show that in a flexible exchange-rate system, a temporary increase in government purchases will cause
A. output and the real interest rate to rise, which increases net exports but has an ambiguous effect on the real exchange rate. B. output to rise and the real interest rate to fall, which reduces net exports and causes the exchange rate to depreciate. C. the real interest rate to fall, which causes the exchange rate to rise, which reduces net exports. D. output and the real interest rate to rise, which reduces net exports but has an ambiguous effect on the real exchange rate.