International trade on the basis of comparative advantage maximizes world output and allows consumers to access better-quality products at lower prices than would be available in the domestic market alone
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
True
You might also like to view...
What is the difference between price discrimination and predatory pricing?
What will be an ideal response?
What is meant by holding all else equal? How is this concept used when discussing movements along the demand curve? How is this concept used when discussing movements along the supply curve?
What will be an ideal response?
Use the following graph for a competitive market to answer the question below.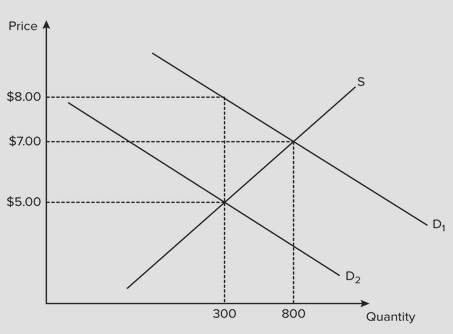 Assume the government imposes a $3 tax on buyers, which results in a shift of the demand curve from D1 to D2. The amount of the tax revenue paid by the seller is
Assume the government imposes a $3 tax on buyers, which results in a shift of the demand curve from D1 to D2. The amount of the tax revenue paid by the seller is
A. $600. B. $300. C. $2100. D. $900.
A nation's technological gains have increased labor productivity and, as a result, the average number of hours worked each week has been falling. How do Gross Domestic Product (GDP) calculations account for this shortening of the average workweek?
A. Gains in leisure time are dollar-valued and included in real per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) gains. B. Gains in leisure time are not included in Gross Domestic Product (GDP), so any increase in real per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) will understate the nation's actual economic growth. C. Neither real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) nor per capita real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) includes the increase in leisure time that results, so the nation's actual economic growth will be overstated. D. Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) does not factor in an increase in leisure time but per capita real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) does.