What is the difference between nominal and real economic variables? Why do economists tend to concentrate on changes in real magnitudes?
What will be an ideal response?
Nominal variables are in units of money, while real variables are in physical quantities of output. We measure nominal variables using current market prices and real variables using market prices in a given base year. Nominal variables may increase, but you don't know if the increase is due to higher prices and the same quantity, or a higher quantity with unchanged prices; real variables reflect just quantity changes. For the most part, real variables (consumption, investment, and the capital stock) affect each other in the economy, with lesser roles played by nominal variables (money supply, and price level).
You might also like to view...
Deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance are all ways in which insurance companies can address the problem of moral hazard
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Financial disintermediation occurs when:
a. Individuals withdraw funds from financial intermediaries and invest them elsewhere. b. Businesses no longer issue stock. c. Individuals no longer trade securities in the secondary market. d. None of the above. e. Businesses no longer borrow directly in the bond market.
Present value calculations allow one to determine the
A. present-day costs and/or benefits of various options. B. social cost of financial calculations. C. return to an uncertain asset. D. real wage. E. utility value of a particular option.
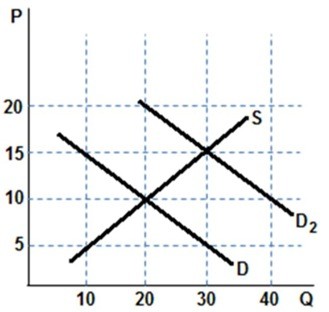 Assume the graph shown represents the market for bottles of wine and was originally in equilibrium with D and S. Something changes and demand shifts to D2. Which of the following is true?
Assume the graph shown represents the market for bottles of wine and was originally in equilibrium with D and S. Something changes and demand shifts to D2. Which of the following is true?
A. Equilibrium quantity increased by 20. B. Equilibrium price increased by $5. C. Equilibrium quantity increased by 30. D. Equilibrium price increased by $15.