One of the advantages of charge-coupled devices over photographic plates is that a CCD can record bright and faint objects on the same exposure
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
T
You might also like to view...
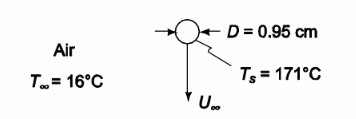
In a lead-shot tower, spherical 0.95-cm-diameter BB shots are formed by drops of molten lead which solidify as they descend in cooler air. At the terminal velocity, i.e., when the drag equals the gravitational force, estimate the total heat transfer coefficient if the lead surface is at 171°C, the surface of the lead has an emissivity of 0.63, and the air temperature is 16°C. Assume CD = 0.75 for the first trial calculation.
GIVEN
• Spherical lead-shot falling through the air at terminal velocity
• Shot diameter (D) = 0.95 cm = 0.0095 m
• Lead surface temperature (Ts) = 171°C = 494 K
• Lead surface emissivity (?) = 0.63
• Air temperature (T?) = 16°C 289 K
• Assume CD = 0.75 for the first trial calculation FIND
• The total average heat transfer coefficient (htotal). ASSUMPTIONS
• The surroundings act as a black body enclosure at T?
SKETCH
This graph shows how the time dilation factor (t?/t) depends on the speed of an object moving by you. How fast does an object have to be moving for you to see its time running about 20% slower than normal (about 80% of normal)?
A) 0.6c B) 0.2c C) 0.8c D) None of the choices are correct; time must be the same for everyone.
A bar magnet is attached solidly to a frictionless surface and its length is aligned with the x axis. To the right of the first magnet a short distance away is a second bar magnet with its center placed on the x axis and its length perpendicular to the x axis. The second magnet is free to move. Once placed in position at rest, which best describes the initial motion of the second magnet?
a. The magnet will move away from the fixed magnet. b. The magnet will not move. c. The magnet will move toward the fixed magnet. d. The magnet will start to rotate.
A circuit consists of three identical lamps connected to a battery as in Figure OQ28.14. The battery has some internal resistance. The switch S, originally open, is closed. What happens to the potential difference across lamp C?