How did the international monetary system created at Bretton Woods in 1944 allow its members to reconcile their external commitments with their internal goals of full employment and price stability?
What will be an ideal response?
As the world economy evolved in the years after World War II, the meaning of "external balance" changed and conflicts between internal and external goals increasingly threatened the fixed exchange rate system. The United States, the issuer of the principal reserve currency, was a major concern, leading to proposals to reform the system.
You might also like to view...
Monopolistically competitive firms have monopoly power because they
A) face downward sloping demand curves. B) are great in number. C) have freedom of entry. D) are free to advertise.
Aggregate expenditure (AE) equals
a. C + I + G. b. C + G. c. C – I – (X – IM). d. C + I + G + (X – IM).
Which of the following is most important if a country is going to achieve and sustain rapid economic growth?
a. large government expenditures as a share of GDP b. institutions and policies that are supportive of competition (open markets) and freedom of exchange. c. free elections and political democracy d. monetary policy makers who are willing to expand the supply of money rapidly
Based on the graph showing the effects of a government budget surplus, a budget surplus would lead to ______.
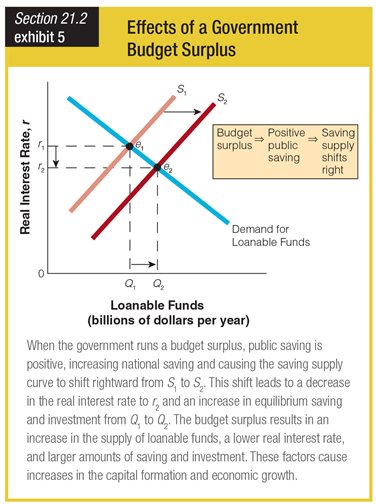
a. a shift in the demand curve for loanable funds to the right
b. a shift in the supply curve for loanable funds to the left
c. a decrease in loanable funds from Q2 to Q1
d. an increase in loanable funds from Q1 to Q2