A CD with a diameter of 12.0 cm starts from rest and with a constant angular acceleration of 1.0 rad/sec2 acquires an angular velocity of 5.0 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.0 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the centripetal acceleration of a point 4.0 cm from the center at the time 2.0 seconds from the start?
A. 0.37 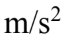
B. 0.30 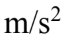
C. 0.28 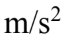
D. 0.21 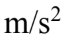
E. 0.16 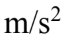
E. 0.16 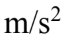
You might also like to view...
When the Sun generates its own energy, it uses weak forces to bind together atomic nuclei
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
What type of bond is formed whenever atoms share a pair of electrons?
a. covalent b. hydrogen c. ionic d. double e. peptide
Reactance: A pure inductor is connected to an ac power supply. In this circuit, the current
A. leads the voltage by 90°. B. is in phase with the voltage. C. lags the voltage by 45°. D. lags the voltage by 90°. E. leads the voltage by 45°.
A cylinder containing an ideal gas has a volume of 2.6 m3 and a pressure of 1.5 × 10^5 Pa at a temperature of 300 K. The cylinder is placed against a metal block that is maintained at 900 K and the gas expands as the pressure remains constant until the temperature of the gas reaches 900 K. The change in internal energy of the gas is +6.0 × 10^5 J. How much heat did the gas absorb?
a. 0 b. 3.4E+5 J c. 6.0E+5 J d. 1.4E+6 J e. 7.8E+5 J