Refer to the diagram of the market for money. The downward slope of the money demand curve D m is best explained in terms of the:
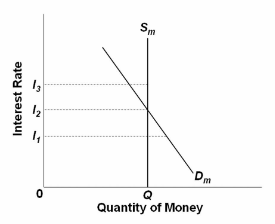
A. transactions demand for money.
B. direct or positive relationship between bond prices and interest rates.
C. asset demand for money.
D. wealth or real-balances effect.
C. asset demand for money.
You might also like to view...
If the price elasticity of demand for a good is 2, then a 10 percent increase in the price of that good ________ the quantity demanded by ________ percent
A) increases; 20 B) decreases; 2 C) decreases; 10 D) decreases; 20 E) increases; 8
Suppose GE produces 1 million light bulbs per month While labor is variable both in the short run and the long run, capital is fixed in the short run. Labor is sold at a rate w and capital is rented at a rate r. a. On a graph with labor on the horizontal axis, illustrate the current isocost and isoquant for GE. Carefully label the slope of the isocost. b. For the rest of the problem, suppose a new tax on capital is implemented but GE intends to continue to produce 1 million light bulbs per year. What will GE do differently in the short run and the long run? Explain using your graph from part (a). c. Using your answer to part (b), explain what happens to the short run cost curve in the short run. What happens to this short run curve in the long run? Do costs rise more or less in the
long run than they do in the short run? d. Do total costs rise more or less in the long run than total expenditures do in the short run? Explain. What will be an ideal response?
With deflation, people will
A. delay their purchases of goods in hopes prices will fall further. B. feel compelled to borrow money. C. see their paycheck rise as bosses seek to reward high performers. D. buy goods earlier than they had originally planned.
Refer to the diagram and list of assumptions. The elimination of gender discrimination:
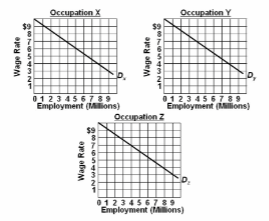
(1) the labor force is comprised of 9 million men and 9 million women workers;
(2) the economy has 3 occupations, X, Y, and Z, each having identical demand curves for
labor; (3) men and women workers are homogeneous with respect to their labor-market
capabilities; (4) women are discriminated against by being excluded from occupations X and Y
and are confined to Z; and (5) aside from discrimination, the economy is competitive, and
workers seek to maximize their earnings.
A. may either increase or reduce real domestic output, depending on what happens to the
level of wages.
B. will increase real domestic output.
C. will have no effect on real domestic output.
D. will reduce real domestic output.