The Canadian experience with inflation and unemployment in the early 1990s has this to say about policy rules:
A) A central bank independent of political pressure may thereby not be serving the public's politically-revealed preferences.
B) A central bank bowing to political pressure cannot get the inflation rate below the unemployment rate.
C) A constant-growth-rate-of-money rule cannot stabilize inflation if unemployment is allowed to vary substantially.
D) A constant-growth-rate-of-high-powered-money rule allows too much variation in the growth of the actual money supply to hold down inflation.
A
You might also like to view...
The type of tax receipts that has shown the slowest growth since World War II has been
A) personal taxes. B) contributions for social insurance. C) taxes on production and imports. D) corporate taxes.
If the labor supply curve is upward-sloping, an adverse supply shock causes ________ in employment and ________ in the real wage
A) no change, a decrease B) a decrease, a decrease C) a decrease, no change D) a decrease, an increase E) an increase, an increase
Total surplus:
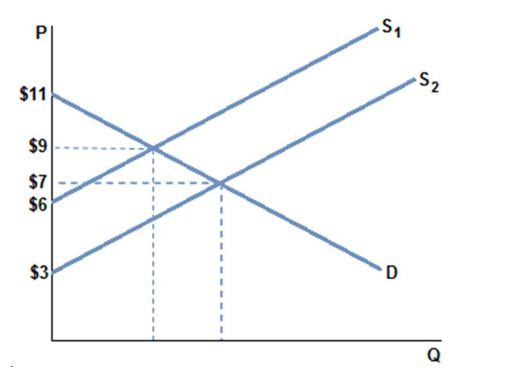
A. is producer and consumer surplus combined.
B. is producer surplus minus consumer surplus.
C. is consumer surplus minus producer surplus.
D. is the total amount spent on a good in a market.
Figure 9-2
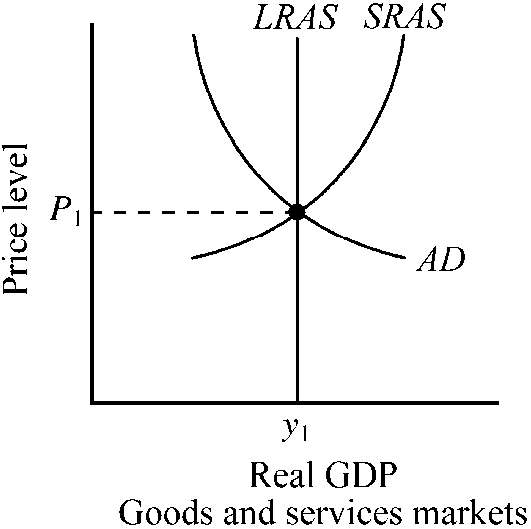
Which of the following is true for the economy depicted in ?
a.
Potential output exceeds y1.
b.
When output y1 is achieved, the actual rate of unemployment will exceed the natural rate of unemployment.
c.
When output y1 is achieved, the actual rate of unemployment will be less than the natural rate of unemployment.
d.
When output y1 is achieved, the actual rate of unemployment will equal the economy's natural rate of unemployment.