A 3.0-kg object moving in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional elastic collision with a 5.0-kg object initially at rest. After the collision the 5.0-kg object has a velocity of 6.0 m/s in the positive x direction. What was the initial speed of the 3.0 kg object?
a. 6.0 m/s
b. 7.0 m/s
c. 4.5 m/s
d. 8.0 m/s
e. 5.5 m/s
d
You might also like to view...
About where is our solar system located within the Milky Way Galaxy?
A) at the center of the galaxy B) about 10 percent of the way from the center of the galaxy to the outskirts of the galactic disk C) about half way from the center of the galaxy to the outskirts of the galactic disk D) near the far outskirts of the galactic disk E) in the halo of the galaxy above the galactic disk
Waves propagate at 7.40 m/s along a stretched string. The end of the string is vibrated up and down once every 2.25 s. What is the wavelength of the waves that travel along the string?
a. 4.50 m b. 16.7 m c. 3.29 m d. 37.5 m e. 8.09 m
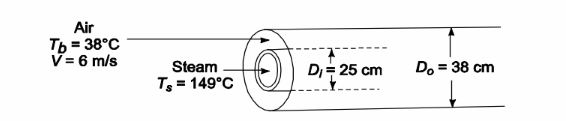
Atmospheric pressure air is heated in a long annulus (25-cm-ID, 38-cm-OD) by steam condensing at 149°C on the inner surface. If the velocity of the air is 6 m/s and its bulk temperature is 38°C, calculate the heat transfer coefficient.
GIVEN
Atmospheric flow through an annulus with steam condensing in inner tube
Inside diameter (Di) = 25 cm = 0.25 m
Outside diameter (Do) = 38 cm = 0.38 m
Steam temperature (Ts) = 149°C
Air velocity (V) = 6 m/s
Air bulk temperature (Tb) = 38°C
FIND
The heat transfer coefficient (hc)
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Steam temperature is constant and uniform
Heat transfer to the outer surface is negligible
Air temperature given is the average air temperature
Thermal resistance of inner tube wall and condensing steam is negligible (Inner tube wall surface
temperature = Ts)
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at 38°C
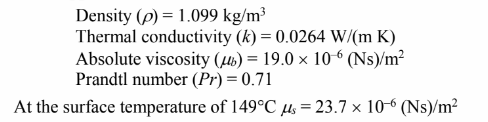
An object starts with an initial velocity of 4.0 m/s and accelerates with an acceleration of +4.0  for 6.0 seconds. It then decelerates at -2.0
for 6.0 seconds. It then decelerates at -2.0  until its velocity is 4.0 m/s. The total distance covered is
until its velocity is 4.0 m/s. The total distance covered is
A. 67 m. B. 94 m. C. 105 m. D. 192 m. E. 215 m.