When a monopolist sells the same product at different prices and the prices are NOT related to cost differences, we have
A. monopoly pricing.
B. marginal cost pricing.
C. price differentiation.
D. price discrimination.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Inflation is
A) a decline in the total purchasing power of an economy. B) a decrease in the amount of other goods that a unit of money will purchase. C) a fall in people's real incomes. D) an increase in the cost of living. E) all of the above.
While the discount rate is "established" by the regional Federal Reserve Banks, in truth, the rate is determined by
A) Congress. B) the president of the United States. C) the Senate. D) the Board of Governors.
In a labor-market pooling equilibrium with high-skill and low-skill workers and where a costly educational degree is used as a signaling device, all else equal, an increase in the wage differential between high- and low-skill workers leads to
A) an increase in the required minimum share of high-skill workers. B) a decrease in the required minimum share of high-skill workers. C) no change in the required minimum share of high-skill workers. D) None of the above answers are correct.
Figure 2-5 shows five different combinations of rockets and cruise ships that a country could manufacture. The production possibilities frontier that is illustrated in Figure 2-5 exhibits
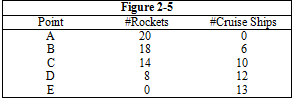
a. decreasing opportunity cost
b. increasing opportunity cost
c. constant opportunity cost
d. zero opportunity cost
e. heightened opportunity cost