Opportunity cost is the value of
A) the best (or most highly valued) forfeited alternative.
B) the chosen alternative.
C) a free good.
D) all forfeited alternatives.
A
You might also like to view...
According to the textbook application, the EPA reported in 1993 that
a. secondhand smoke was a carcinogen b. secondhand smoke was prohibited from public places c. secondhand smoke did not pose a human health risk d. none of the above
________ are asymmetric information problems that act as a barrier to efficient allocation of capital
A) Asset prices B) Credit imbalances C) Financial frictions D) Financial derivatives
Suppose a bond has a coupon of $75, face value of $1000, and current price of $1100. What is the coupon rate? What is its current yield? Report a percentage with two decimal places
What will be an ideal response?
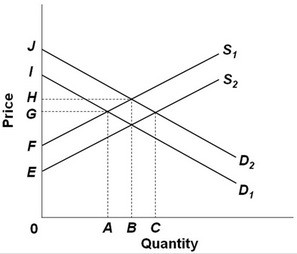 Refer to the above supply and demand graph. Point A represents the current equilibrium level of output of this product and point B represents the optimal level of output from society's perspective. If government decides to correct this spillover problem by subsidizing producers, then the:
Refer to the above supply and demand graph. Point A represents the current equilibrium level of output of this product and point B represents the optimal level of output from society's perspective. If government decides to correct this spillover problem by subsidizing producers, then the:
A. demand curve will shift from D2 to D1. B. supply curve will shift from S1 to S2. C. supply curve will shift from S2 to S1. D. demand curve will shift from D1 to D2.