Graded motor unit recruitment is important to allow for coordinated movement to occur. According to Henneman's Size Principle, which motor units would be recruited first when voluntarily activated?
a. Type IIa
b. Type IIb
c. Type I
d. All of the above
Answer: c. Type I
You might also like to view...
The two types of secondary structure interactions are referred to as:
A. primary and secondary. B. amide and carbonyl. C. residual and permanent. D. -helix and -sheet. E. sulfhydryl and phosphatidic.
B cells and T cells make up which part of the immune system?
a. natural immune system b. acquired immune system c. adaptive immune system d. innate immune system
Which of the following is NOT an example of
biological digestion?
a. chewing a piece of chocolate b. the breaking up of proteins by stomach acid c. salivary enzymes hydrolyzing starch into glucose d. absorption of fatty acids in the small intestines e. all of these are examples of biological digestion
The sliding filament model for muscle contraction can be studied using an isolated skeletal muscle that is fixed at each end, while a machine records the tension that is generated when the muscle is stimulated to contract. In one particular muscle tested, the length of the thick filaments was 1.6 ?m, and the length of the thin filaments that project in from each Z line toward the center of the sarcomere was 1.0 ?m. A summary of the results comparing sarcomere length to the degree of tension produced during contraction is shown below. What most likely explains the difference between segment II and segment III of the graph?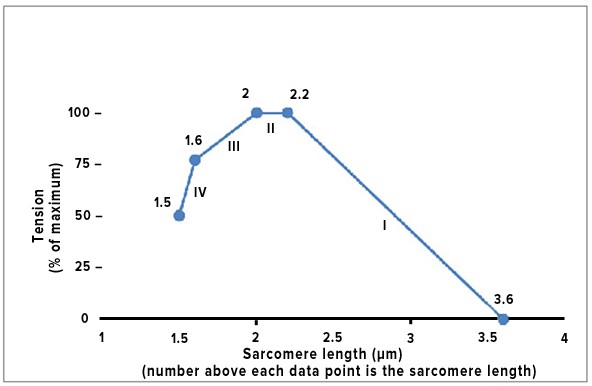
A. There is an increasing overlap of the free ends of the thin filaments in segment III but not in segment II. B. The distance between the Z lines is constant in segment II but rapidly increasing in segment III. C. Fewer myosin cross-bridges are forming in segment II than in segment III. D. The muscle cells used up all the ATP by the end of segment II. E. The length of the thin filaments is decreasing in segment III but not in segment II. F. The length of the thick filaments is decreasing in segment III but not in segment II.