Contrast the economic performance of the American economy of 2001 with the economic performance of the 1996 to 2001 period. Use the appropriate aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves to distinguish the differing economic condition of the two periods
The economic performance of the 1996 to 2000 period could be characterized as a fortuitous combination of increasing aggregate demand at the same time the aggregate supply curve was shifting out as well. This created both economic growth and a fairly stable price level. The American economy experienced both low inflation and decreasing rates of unemployment. The year 2001 represents a classic aggregate demand-caused recession. A decrease in investment spending caused a decrease in aggregate demand. This caused a decrease in output and employment while putting downward pressure on prices. The American economy suffered the usual effects of recession, proving that the United States is not immune from the normal vicissitudes of the business cycle and that the U.S. had not entered a "new paradigm."
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax increase that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies.
A. D; C B. D; B C. A; B D. B; C
In the United States, monetary policy is determined by
A) the Federal Reserve. B) the president. C) private citizens. D) the Treasury Department.
A graph which maps the total costs of production against the amount made is called the
A. average cost function. B. production function. C. marginal cost function. D. cost function.
When price is $8
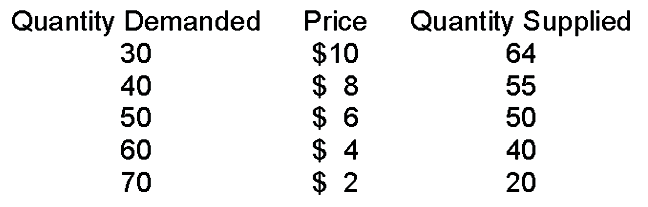
A. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must fall to get to equilibrium price.
B. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium price.
C. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded and, therefore, price must fall to get to equilibrium price.
D. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium price.