Exhibit 1A-2 Straight line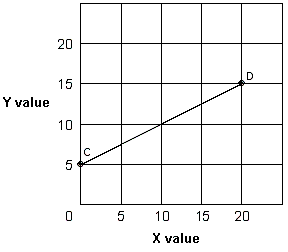
In Exhibit 1A-2, explain the slope of straight line CD.
A. As the X value increases by 20, the Y value increases by 5, so the slope is 4.
B. As the Y value increases by 5, the X value increases by 20, so the slope is 1/4.
C. As the X value increases by 10, the Y value increases by 5, so the slope is 2.
D. As the Y value increases by 5, the X value increases by 10, so the slope is 1/2.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
What is meant by the marginal rate of transformation?
What will be an ideal response?
Explicit agreements between businesses to keep prices high:
A. are illegal. B. are called collusion. C. are not in the public's best interests. D. All of these statements are true.
Micromania imports a good costing it $12,000 and exports a different good for a price of $9,000 . Ten years ago it paid $6,000 for the good and received $3,000 for the good it exported. How has the terms of trade index changed from then to now?
a. From 25 to 75 b. From 66 to 300 c. From 75 to 25 d. From 300 to 66 e. None of the above
Table 1.2 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of Stealth bombers and B-1 bombers that might be produced in a year with the limited U.S. capacity, ceteris paribus.Table 1.2Production Possibilities for BombersCombinationNumber of B-1 BombersOpportunity cost(Foregone Stealth)Number of Stealth BombersOpportunity cost (Foregone B-1)A20NA195 B35 180 C45 150 D50 100NAThe lowest opportunity cost in Table 1.2 for Stealth Bombers is
A. 10 B-1 bombers B. 3 B-1 bombers C. 2 B-1 bombers D. 4 B-1 bombers