What happens to the marginal cost curve when the marginal physical product of labor is rising?
A. It becomes vertical.
B. It becomes downward sloping.
C. It becomes horizontal.
D. It becomes upward sloping.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 50 percent chance of being $6 and a 50 percent chance of being $8. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
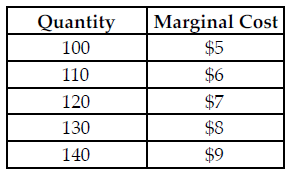
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
A) 110
B) 140
C) 130
D) 120
If the market price of a product falls and as a result total revenue of firms falls, we can conclude that
A) demand is elastic in this price range. B) the product's price is above the midpoint of its demand curve. C) demand is inelastic in this price range. D) the demand curve is horizontal.
Externalities exist because
A) private costs differ from social costs. B) private costs are equal to social costs. C) government has created them. D) they are a function of socialism.
"Wine experts are discovering that California wines of several varieties and vintages are comparable to many of the best French wines. The result is an increased demand, here and abroad, for California wines." With regard to the U.S. balance on current account, this trend will
a. increase the U.S. deficit because of the rise in the price of California wine. b. decrease the U.S. deficit because of increased shipments of California wines abroad. c. decrease the demand for U.S. dollars. d. increase the U.S. demand for euros.