An underground water main burst in Manhattan and flooded the building where Acme Inc. has an electricity supply substation. A fire resulted and disrupted electric power for four days. This occurred during the biannual "Buyers Week," when merchandisers from around the world were in town to visit fashion showrooms and place orders for future seasons. Around 200 merchandisers brought suit against Acme. Some of the businesses had no direct contractual relationship with Acme. They argued that their lease agreements with their landlords, who were the direct contracting entities with Acme, obligated them to pay a share of the electricity expenses and therefore they could sue under the contract agreement between the landlords and Acme. Are the demands of the businesses with no direct contractual
relationship with Acme justified?
What will be an ideal response?
The plaintiffs (the businesses who had no direct contractual relationship with Acme) cannot seek recovery as third-party beneficiaries of the contract. Acme did not expressly undertake to supply electricity to them. They were incidental beneficiaries of their landlords' contracts and thus do not have a claim.
You might also like to view...
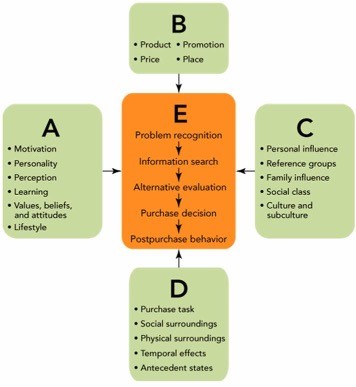 Figure 4-4In Figure 4-4 above, B represents the ________ influences that can affect the consumer purchase decision process.
Figure 4-4In Figure 4-4 above, B represents the ________ influences that can affect the consumer purchase decision process.
A. situational B. economic C. market dominated D. environmental E. marketing mix
______ are monetary damages awarded by the court that are designed to punish an injuring party that has intentionally inflicted harm on others.
A. Undue hardship B. Affirmative actions C. Reasonable damages D. Punitive damages
Proposals related to ________ include promoting the use of sustainable ingredients, recycling and reducing solid wastes, and managing energy consumption
A) the right to be informed B) consumer protection C) preserving the world for future consumption D) quality of life E) the right to charge any price for the product
Ethics and law are unrelated
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false