Strictly speaking, from the point of view of a person on the ground floor of a tall skyscraper, a person at the top ages
1) more slowly,
2) faster,
3) the same,
and from the point of view of a person at the top of the skyscraper, the person at the ground level ages
4) more slowly.
5) faster.
6) the same.
Answer: 2, 4
You might also like to view...
A proton initially moves left to right along the x axis at a speed of 7.0 × 10^3 m/s. It moves into an electric field, which points in the negative x direction, and travels a distance of 0.70 m before coming to rest. What acceleration magnitude does the proton experience?
a. 7.0E+3 m/s2 b. 3.5E+7 m/s2 c. 1.8E+9 m/s2 d. 1.4E+12 m/s2 e. 2.5E+9 m/s2
Two identical objects are released from rest from heights R and 2R above the surface of the Earth. After traveling a distance R/2, which object has the larger energy?
Photoelectric Effect: Monochromatic light is incident on a metal surface, and the ejected electrons give rise to a current in the circuit shown in the figure. The maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons is determined by applying a reverse ('stopping') potential, sufficient to reduce the current in the ammeter to zero. If the intensity of the incident light is increased, how will the required stopping potential change?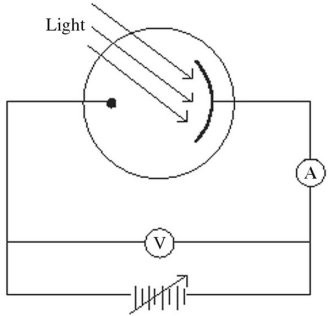
A. It will remain unchanged. B. It will increase. C. It will decrease.
Observers in all reference frames will agree (perhaps by tracking individual electrons) that the bar’s left side becomes negatively charged and its right side becomes positively charged, meaning that just after the bar begins to move (but before the charges have time to pile up at the ends) some leftward electromagnetic force must have been acting on the bar’s electrons. What type of force is this 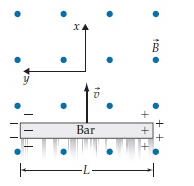 in the implied reference frame of the diagram above?
in the implied reference frame of the diagram above?
A. The force is purely electric. B. The force is purely magnetic. C. The force is both electric and magnetic. D. There is no force on the bar’s electrons in this frame.