If the purchasing power of the dollar is less than the purchasing power of the British pound, purchasing power parity predicts that the exchange rate will
A) decrease if the exchange rate is less than 1 pound per dollar.
B) be equal to the relative purchasing power across the currencies in the long run.
C) increase if the exchange rate is greater than 1 pound per dollar.
D) All of the above are correct.
B
You might also like to view...
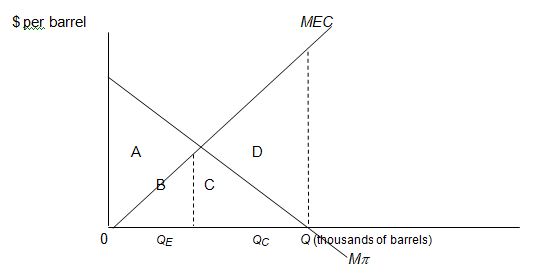
Give the economic interpretation of each of the labeled areas: A, B, C, and D.
Use the following graph of the refined petroleum market to answer the questions below.
The demand for loanable funds curve shows the
A) positive relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds demanded. B) positive relationship between the demand for loanable funds curve and the supply of loanable funds curve. C) U-shaped relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds demanded. D) negative relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds demanded. E) negative relationship between the demand for loanable funds curve and the supply of loanable funds curve.
Price discrimination is when a firm charges:
A. the same price to all consumers. B. different prices for different goods to different consumers. C. different prices for the same goods to different consumers. D. None of these is correct.
An increase in the saving rate in a steady-state economy would cause
A. a rightward movement along the saving-per-worker curve and an increase in the capital-labor ratio. B. a downward shift in the saving-per-worker curve and a decrease in the capital-labor ratio. C. an upward shift in the saving-per-worker curve and an increase in the capital-labor ratio. D. a leftward movement along the saving-per-worker curve and a decrease in the capital-labor ratio.