When a liquid boils and changes to a gas, it is said to have undergone a change of ________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
phase
You might also like to view...
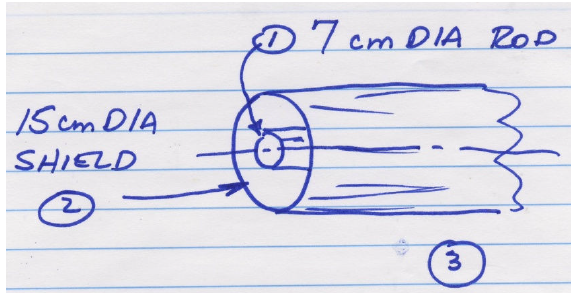
A 7 cm diameter heat exchanger rod at 400ºC is surrounded by a 15 cm diameter heat shield. If the surroundings are a black body at 20ºC, determine the equilibrium temperature of the shield if (a) both rod and shield are black bodies, (b) emissivity of both is 0.7, and (c) the rod is a black body and the shield has emissivity of 0.7.
A friend tells you that he knows of a situation in which bowl of ice sitting by itself on a table in a room whose air temperature is 20oC gives up heat the surrounding air. What’s wrong with this concept?
A. It would violate the 0th law of thermodynamics B. It would violate the 1st law of thermodynamics C. It would violate the 2nd law of thermodynamics D. It would violate the 3rd law of thermodynamics
Power: A series circuit has a 100-? resistor, 4.00-mH inductor and a 0.100-?F capacitor connected across a 120-V rms ac source at the resonance frequency. What is the power dissipated by the circuit?
A. 100 W B. 120 W C. 144 W D. 160 W E. 45.8 W
What is the acceleration of a rock thrown straight upward on the way up? At the top of its flight? On the way down?
A. The acceleration of the rock thrown upward has the same value of 7.2 m/s-sq downwards at all three points of the rock on way up, stationary at the top of its flight and on way down. The magnitude and direction of the velocity of the rock will not change but the acceleration will remain different in magnitude and direction. B. The acceleration of the rock thrown upward has the same value of - 9.8 m/s2 downwards at all three points of the rock on way up, stationary at the top of its flight and on way down. The magnitude and direction of the velocity of the rock will be changing but the acceleration will remain the same in magnitude and direction throughout its trip. C. The acceleration of the rock thrown downwards has the same value of 5 m/s-sq downwards at all three points of the rock on way up, stationary at the top of its flight and on way down. The magnitude and direction of the velocity of the rock will be changing but the acceleration will remain the same in magnitude and direction throughout its trip.