Explore DNS Query Traffic
Wireshark is an open source packet capture and analysis tool. Wireshark gives a detailed breakdown of the network protocol stack. Wireshark allows you to filter traffic for network troubleshooting, investigate security issues, and analyze network protocols. Because Wireshark allows you to view the packet details, it can be used as a reconnaissance tool for an attacker.
In this lab, you will install Wireshark on a Windows system and use Wireshark to filter for DNS packets and view the details of both DNS query and response packets.
Required Resources
? 1 Windows PC with Internet access and Wireshark installed
Instructor Note: Using a packet sniffer such as Wireshark may be considered a breach of the security policy of the school. It is recommended that permission is obtained before running Wireshark for this lab. If using a packet sniffer such as Wireshark is an issue,
a. Observe the traffic captured in the Wireshark Packet List pane. Enter udp.port == 53
in the filter box and click the arrow (or press Enter) to display only DNS packets.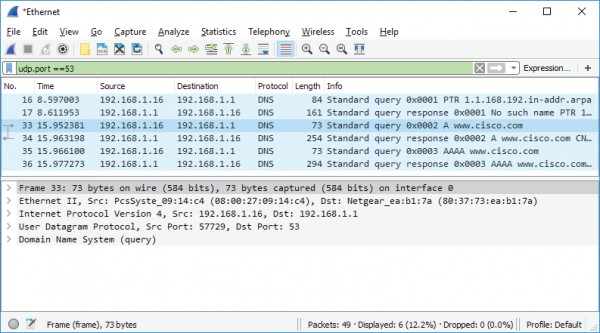
b. Select the DNS packet labeled Standard query 0x0002 A www.cisco.com.
c. In the Packet Details pane, notice this packet has Ethernet II, Internet Protocol Version
4, User Datagram Protocol and Domain Name System (query).
d. Expand Ethernet II to view the details. Observe the source and destination fields.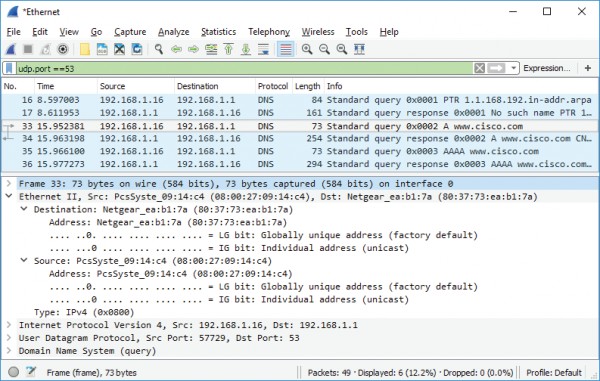
What are the source and destination MAC addresses? Which network interfaces are
these MAC addresses associated with?
In this example, the source MAC address is associated with the NIC on the PC and
the destination MAC address is associated with the default gateway. If there is a local
DNS server, the destination MAC address would be the MAC address of the local DNS
server.
e. Expand Internet Protocol Version 4. Observe the source and destination IPv4
addresses.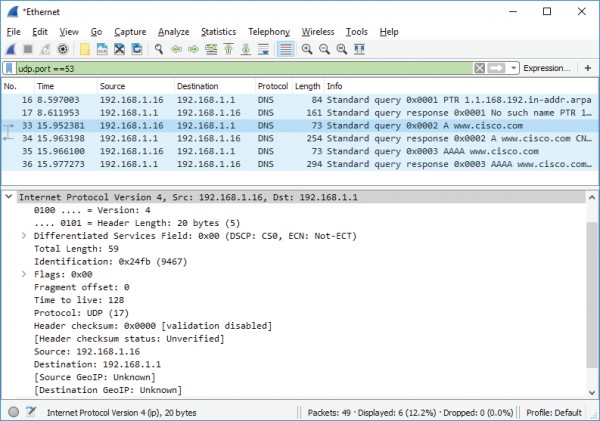
What are the source and destination IP addresses? Which network interfaces are these
IP addresses associated with?
In this example, the source IP address is associated with the NIC on the PC and the
destination IP address is associated with the default gateway.
f. Expand the User Datagram Protocol. Observe the source and destination ports.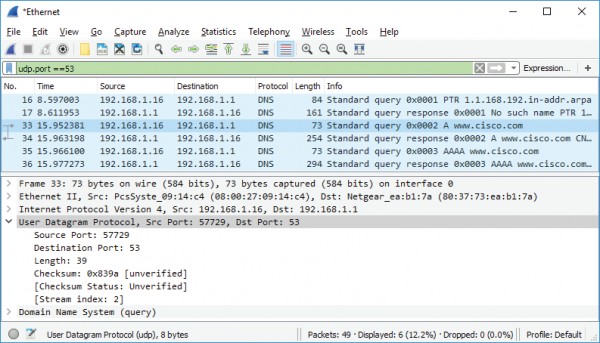
What are the source and destination ports? What is the default DNS port number?
The source port number is 577729 and the destination port is 53, which is the default
DNS port number.
g. Open a Command Prompt and enter arp –a and ipconfig /all to record the MAC and IP
addresses of the PC.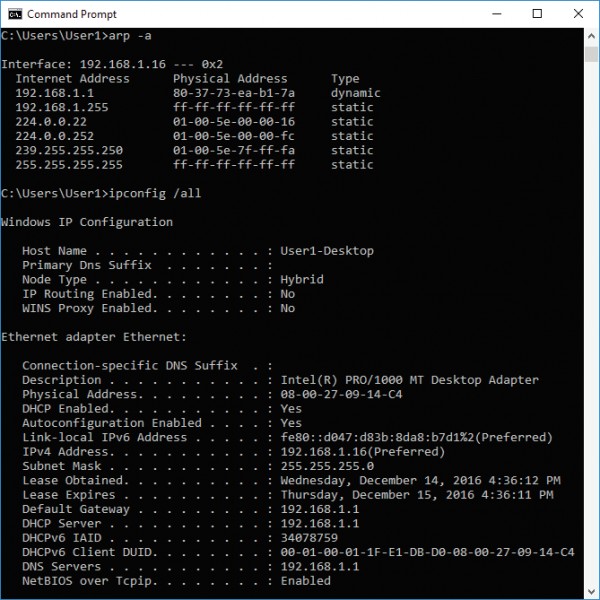
Compare the MAC and IP addresses in the Wireshark results to the results from the
ipconfig /all results. What is your observation?
The IP and MAC addresses captured in the Wireshark results are the same as the
addresses listed in the ipconfig /all command.
h. Expand Domain Name System (query) in the Packet Details pane. Then expand the
Flags and Queries.
i. Observe the results. The flag is set to do the query recursively to query for the IP
address to www.cisco.com.
You might also like to view...
To obtain a parallel stream, simply invoke method ________ on an existing stream.
a. toParallel b. toStream c. parallel d. toParallelStream
Of the three levels of Windows updates, which does Microsoft recommend you not do?
A) Install updates automatically B) Only download updates C) Never check for updates D) Only download updates but let you install them
Methods are also called modules.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Method ____ is called whenever the SeekBar’s thumb position changes.
a. onProgressChanged b. onSeekBarChanged c. onThumbPositionChanged d. onValueChanged