According to the definitions of national saving and public saving, if Y, C, and G remained the same, an increase in taxes would
a. raise national saving and public saving.
b. raise national saving and raise public saving.
c. leave national saving and public saving unchanged.
d. leave national saving unchanged and raise public saving.
d
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 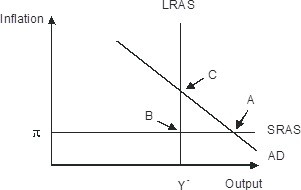
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Starting from long-run equilibrium, an adverse inflation shock results in a short-run equilibrium with ________ inflation and ________ output.
A. lower; lower B. higher; lower C. higher; higher D. higher; potential
Some examples of unconventional monetary policies include massive lending to banks, or even to firms that are nor banks, and open-market purchases of securities other than Treasury bills.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
In the small town of Springfield, Duffman observes that the price of beer has fallen. Duffman concludes that the total amount of money spent buying beer has to fall since the price of beer is lower now. Is he correct? Why or why not? Clearly explain your answer.
What will be an ideal response?