Many antibiotics kill bacteria because they hinder translation by prokaryotic _____.
A. ribosomes
B. capsules
C. cytoskeleton
D. cytoplasm
E. nucleoids
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
· What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
Gather Content
· What do you know about translation? How does it relate to the question?
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
A. ribosomes
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
o The question asks about inhibition of translation.
· What type of thinking is required?
o You are being asked to apply your knowledge of translation to explain how an antibiotic works.
· What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
o Antibiotic – a drug that kills bacteria.
o Translation – conversion of the information in mRNA into protein.
Gather Content
· What do you know about translation? How does it relate to the question?
o Translation occurs when ribosomes pair the anticodon on a transfer RNA with the codon on a messenger RNA. The transfer RNAs each carry an amino acid, and these are joined together to form a protein.
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
o None of the other organelles listed are involved in translation.
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
o If translation is blocked by a drug it most likely affects the ribosome.
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
o This question asked you to apply the role of the ribosome to predict the mechanism by which an antibiotic kills bacteria. If you got the correct answer, great job! If you got an incorrect answer, where did the process break down? Did you remember that translation involved converting mRNA into protein? Did you understand that the ribosome was the enzyme that catalyzed the synthesis of proteins?
You might also like to view...
The transporter indicated by the letter “A” in the
above figure represents a. an active Br transporter. b. a sodium-potassium transporter. c. a passive potassium transporter. d. a calcium-phosphorus transporter. e. none of these.
Why does sweating cool your skin on a hot, dry day but make you feel warmer on a hot, humid day?
What will be an ideal response?
What causes the "leaf drop" that occurs in woody plants in preparation for winter dormancy?
A) Inhibition of gibberellin B) Suppressed auxin production C) Increased chlorophyll development D) Opened stomata E) Increased ethylene production
A 6.85 kb EcoRI fragment of DNA is shown below. The location of several restriction sites is indicated. Scale is approximate.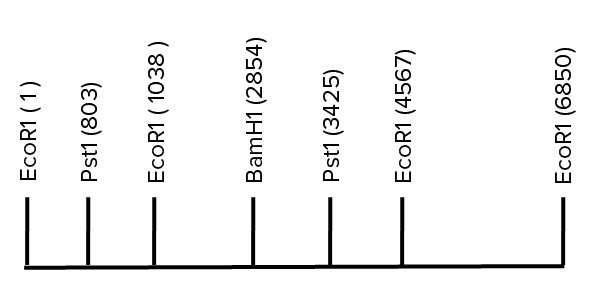 If you were to digest this DNA with PstI, which length of DNA fragment would migrate the fastest on an agarose gel?
If you were to digest this DNA with PstI, which length of DNA fragment would migrate the fastest on an agarose gel?
A. 2622 B. 235 C. 3425 D. 803