A heat-conducting rod that is wrapped in insulation is constructed with a 0.15-m length of alloy A and a 0.40-m length of alloy B, joined end-to-end. Both pieces have cross-sectional areas of 0.0020 m2
The thermal conductivity of alloy B is known to be 1.8 times as great as that for alloy A. The end of the rod in alloy A is maintained at a temperature of 10°C, and the other end of the rod is maintained at an unknown temperature. When steady state flow has been established, the temperature at the junction of the alloys is measured to be 40° C, and the rate of heat flow in the rod is measured at 56 W. What is the temperature of the end of the rod in alloy B? A) 80°C
B) 84°C
C) 88°C
D) 92°C
E) 96°C
B
You might also like to view...
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20 rad/s. During a 5.0-s interval the angular velocity increases to 40 rad/s. Assume that the angular acceleration was constant during the 5.0-s interval. How many revolutions does the wheel turn through during the 5.0-s interval?
a. 20 rev b. 24 rev c. 32 rev d. 28 rev e. 39 rev
Hurricanes derive their energy from
a. gravity. b. specific heat. c. the Coriolis force. d. latent heat.
Two blocks are accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface as shown. Frictional forces keep the two blocks from sliding relative to each other, and the two move with the same acceleration. If F = 1.2 N and M = 1.0 kg, what is the horizontal component (frictional force) of the force of the large block on the small block?
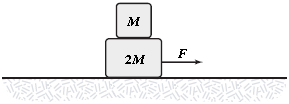
a.
0.40 N to the left
b.
0.80 N to the right
c.
0.40 N to the right
d.
0.80 N to the left
e.
1.20 N to the left
Precession of Earth's axis causes the date at which perihelion of Earth's orbit occurs to slowly change
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false