If American demand for purchases of British goods has decreased, how would you expect the equilibrium exchange rate in the market for dollars to respond? Support your answer graphically
What will be an ideal response?
If Americans are demanding fewer British goods, they will trade fewer dollars in the foreign exchange market for British pounds. This decrease in the supply of dollars is represented by the shift to the left in the supply of dollars below. As the supply of dollars decreases, the equilibrium exchange rate rises (the dollar appreciates).
You might also like to view...
Figure 4-9
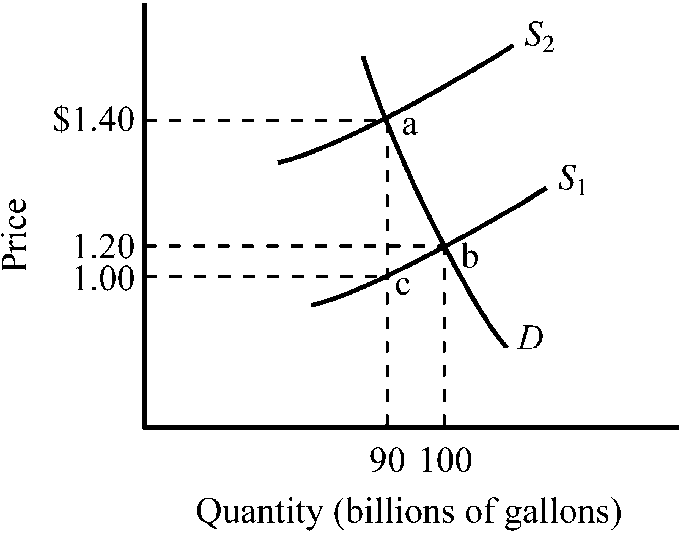
Refer to . The market for gasoline was initially in equilibrium at point b and a $.40 excise tax is illustrated. What does the triangular area abc represent?
a.
the revenue the government derives from the tax
b.
the tax paid by consumers
c.
the tax paid by producers
d.
the deadweight loss (or excess burden) created by the tax
Bryce saw a motorcycle for sale online. He had been wanting that model of motorcycle and was willing to pay $5,000. The one he saw online was listed for $3,500, so he immediately bought it. In this case, how much was the consumer surplus?
a. $1,500 b. $3,500 c. $5,000 d. $8,500
In a perfectly competitive market, individual consumers have _____.
(A) Less influence than producers concerning prices. (B) No influence over determining price. (C) More influence than producers concerning prices. (D) More influence than consumers in other market structures.
In the 1990s the U.S. rate of inflation was held down by each of the following except
A. imported goods. B. the rise of huge discount retailers. C. rising exports. D. the efforts of business firms to raise their efficiency and productivity.