A free electron and a free proton are released in identical electric fields. (i) How do the magnitudes of the electric force exerted on the two particles compare?
1.It is millions of times greater for the electron.
2.It is thousands of times greater for the electron.
3.They are equal.
4.It is thousands of times smaller for the electron.
5.It is millions of times smaller for the electron.
3
You might also like to view...
A circular ice skating rink, 20 m in diameter, is enclosed by a large hemispherical dome of diameter 30 m. Assuming that the ice is 2 cm thick, estimate the time it takes for the ice to melt if the refrigeration system of the rink fails. Make this calculation first with both the dome and the ice behaving as black bodies at respective temperatures of 20°C and 0°C. Then repeat with the water-ice having an emissivity of 0.3 and losing heat by natural convection to the air in the dome with a convection heat transfer coefficient of 15 W/(m2 K).
GIVEN
• Circular skating rink enclosed by hemispherical dome
• Diameter of the rink (D1) = 20 m
• Diameter of hemispherical dome (D2)= 30 m
• Temperature of dome and surrounding air (T2)= 200C
• Temperature of ice (T1) = 00C
FIND
Time it takes for ice to melt if the refrigeration system of rink fails considering (a) both dome and ice behaving as black bodies. (b) ice having emissivity of 0.3 and loosing heat by natural convection to air in dome with 2 15 W/(m K)
SKETCH
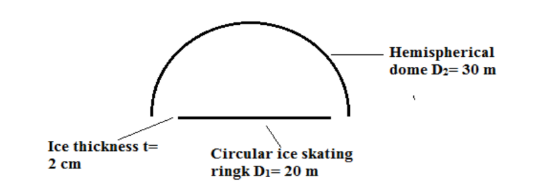
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Latent Stefan-Boltzman’s heat of fusion constant for ice (Lf)= (? 334 KJ/kg )=5.67*10-8 W/(m2 K4)
The galactic center lies in the direction of which constellation?
A) Orion B) the Big Dipper C) Leo D) Sagittarius E) Taurus
Muons at speed 0.9995c are sent round and round a circular storage ring of radius 550 m. If a muon at rest decays into other particles after an average T =2.2 × 10^?6 s, how many trips around the storage ring do we expect the 0.9995c muons to make before they decay?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 12 d. 6 e. 131
If an object accelerates, a force is acting on it
1.True 2.False