If labor-intensive textile products could be produced more cheaply in low-wage countries than in the United States, the United States would gain if it
a. levied a tariff on the goods produced by the cheap foreign labor.
b. subsidized the domestic textile industry so it could compete in international markets.
c. used its resources to produce other items while importing textiles from foreigners.
d. levied a tax on the domestic textile products to penalize the industry for inefficiency.
C
You might also like to view...
Suppose you rent an apartment and are worried about a break-in that results in theft of your property. Suppose your monthly consumption level is currently $4,000 but a break-in would result in you having to finance your purchase of replacement property -- and this would reduce your current consumption to $2,000 per month. There is a 10% chance of a break-in, and your tastes can be modeled with the expected utility form using the function 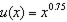
b. How does your answer to (a) change if the probability of a break-in increases to 20%? c. What is the certainty equivalent and the risk premium in each case? d. What equation would you have to solve to get the answer to the following: How much would you be willing to pay to keep the crime rate in your area from increasing (i.e. to keep the probability of a break in to 10% rather than have it rise to 20%) assuming there is no rental insurance available in your area? e. What would you be willing to pay to avoid the increase in the crime rate if there is a full menu of actuarily fair rental insurance available at all times? What will be an ideal response?
In the figure above, ________ is a technologically efficient point
A) d B) f C) g D) None of the selections is correct.
If the monopoly illustrated in the figure above could engage in perfect price discrimination, the deadweight loss would be
A) $0. B) $22.50. C) $90.00. D) $250.00.
An efficient tax is
A) a tax that raises a maximum amount of revenue. B) a tax that imposes a small excess burden relative to the tax revenue that it raises. C) a tax that imposes an equal tax burden on buyers and sellers. D) a tax that is used to fund research and development of new technology.