Conservation of Momentum: You are standing on a skateboard, initially at rest. A friend throws a very heavy ball towards you. You have two choices about what to do with the ball: either catch the ball or deflect it back toward your friend with the same speed as it was originally thrown. Which choice should you make in order to maximize your speed on the skateboard?
A. Catch the ball.
B. Deflect the ball back.
C. Your final speed on the skateboard will be the same regardless whether you catch the ball or deflect the ball.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which is NOT a reason that silicon is unsuitable as a building block for life compared to carbon?
A) silicon—silicon bonds are much weaker than carbon—carbon bonds B) silicon does not form multiple bonds with itself, limiting the complexity of molecules it can form C) silicon does not bond with many other elements D) silicon dioxide is a high melting point solid and, hence, cannot be used to transfer silicon atoms like gaseous carbon dioxide can be used to transport carbon atoms
If an ideal gas does positive work on its surroundings, we may assume, with regard to the gas
a. temperature increases. b. volume increases. c. pressure increases. d. internal energy decreases.
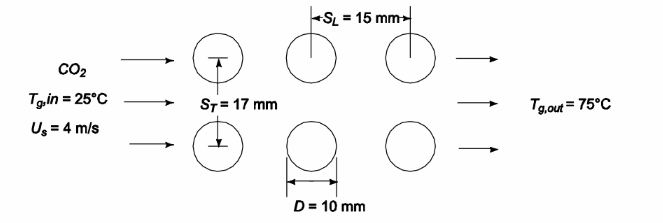
Carbon dioxide gas at 1 atmosphere pressure it to be heated from 25°C to 75°C by pumping it through a tube bank at a velocity of 4 m/s. The tubes are heated by steam condensing within them at 200°C. The tubes have 10 mm OD, are in an in–line arrangement, have a longitudinal spacing of 15 mm and a transverse spacing of 17 mm. If 13 tube rows are required, what is the average heat transfer coefficient and what is the pressure drop of the carbon dioxide?
GIVEN
• In-line tube bank: condensing steam inside, CO2 outside
• CO2 temperatures
? In: (Tg,in) = 25°C
? Out: (Tg,out) = 75°C
• CO2 velocity (Us) = 4 m/s
• Steam temperature (Ts) = 200°C
• Tube outside diameter (D) = 10 mm = 0.01 m
• Longitudinal spacing (SL) = 15 mm = 0.015 m
• Transverse spacing (ST) = 17 mm = 0.017 m
• Number of tubes (N) = 13
FIND (a) The average heat transfer coefficient (hc) (b) The CO2 pressure drop (?p)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• The thermal resistances of the condensing steam and the tube walls are negligible (tube wall temperature = Ts)
SKETCH
A child pulls a 3.00-kg sled across level ground at constant velocity with a light rope that makes an angle 30.0° above horizontal. The tension in the rope is 5.00 N. Assuming the acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s2, what is the coefficient of friction between the sled and the ground?
A) 0.161
B) 0.188
C) 0.0441
D) 0.0851
E) 0.103