The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 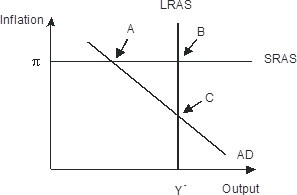
A. recessionary; B
B. recessionary; C
C. recessionary; A
D. expansionary; A
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________. 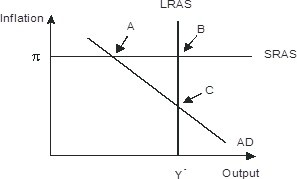
A. Rising; A B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; B: C D. Rising; A; C
Graphically illustrate the intended effect of this tax incentive, and explain the expected outcome of phasing it out. (Assume there is no production externality.)
To promote cleaner air, the federal government in the United States enacted tax incentives for purchasing new electric vehicles or clean-fuel vehicles. These were scheduled to be phased out over time.
Firms in an oligopoly market will have a more difficult time maintaining price coordination when:
A) demand for the firms' products remains stable. B) the firms' cost structures are similar. C) the firms' products are highly differentiated. D) each firm controls the same share of the market.
The reason relative purchasing power parity (RPPP) is better at predicting exchange rates than absolute purchasing power parity (APPP) is because:
a. Actually, it is the other way around. APPP has been shown empirically and theoretically to be a more accurate way to predict exchange rates. b. APPP deals only with countries that have some sort of imbalance like hyperinflation. RPPP deals with any and all countries, which makes the job of predicting exchange rates easier. c. APPP has to begin and end in parity. RPPP just requires that the initial disequilibrium remain the same. d. APPP predictions are often biased because of central bank controls, sticky prices, and protectionism. RPPP can abstract from these problems.