In Figure 23.1, for a good with no externality, which area represents the producer surplus? 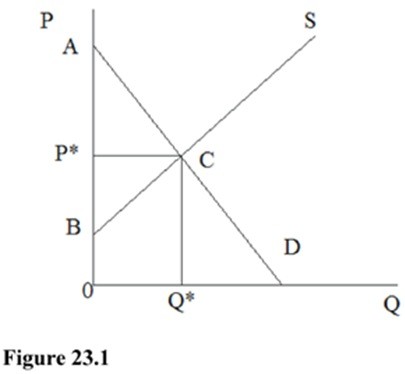
A. 0P*CQ*
B. 0BCQ*
C. ABC
D. BP*C
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The stock of high-powered money in the economy is $80 billion. The bank reserve-holding ratio is 0.12 and the public wishes to hold 10% of its deposits as cash. The money supply will be approximately
A) $363 billion assuming the 80 billion of high-powered money is held by banks. B) $400 billion assuming the 80 billion of high-powered money is held by the Fed or in bank vaults. C) $327 billion assuming the 80 billion of high-powered money is not held by the Fed or in bank vaults. D) $425 billion assuming the 80 billion of high-powered money is held by banks.
Figure 18-2
A. 0 percent B. 20 percent C. 50 percent D. 80 percent
Which of the following statements best describes the price, output, and profit conditions of monopolistic competition?
A. Price will equal marginal cost at the profit-maximizing level of output; profits will be positive in the long-run. B. Price will always equal average variable cost in the short run and either profits or losses may result in the long run. C. Marginal revenue will equal marginal cost at the short run, profit-maximizing level of output; in the long run, economic profit will be zero. D. Marginal revenue will equal average total cost in the short run; long-run economic profits will be zero.
Suppose two countries make a credible commitment to fix their bilateral exchange rate. In such a situation, we know that
A) the uncovered interest parity condition no longer holds. B) the real exchange rate must be constant as well. C) each country can freely allow its interest rate to diverge from that of the other country. D) the interest rate in the two countries must be equal. E) neither country will run a trade deficit.