Paul Romer's theory of economic growth differs from traditional theories in that
A. Romer argues that investment in capital goods is not important in encouraging growth while investment in human capital is, whereas traditional theorists emphasize both human and physical capital.
B. Romer argues an investment-knowledge cycle allows a one-time increase in investment to permanently increase a country's growth rate, while traditional theory argued such an investment would have only a short-term effect.
C. Romer argues that investment in human capital always occurs before investment in physical capital, while traditional theories emphasize the priority of physical capital.
D. Romer argues an investment-knowledge cycle can exist, but requires constant increases in investment rates, while traditional theories argue that investment rates can be constant.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose that last week 100,000 people lost their jobs or quit. We can say that
A) the number of unemployed increased by less than 100,000 people because we should not count those who quit their jobs. B) the 100,000 people represent a stock known as the new unemployed. C) the number of unemployed increased by 100,000 people. D) the 100,000 people represent a flow known as job departures.
Suppose a perfectly competitive market is in long-run equilibrium with a price of $12. Then there is a permanent increase in demand
As a result, in the short run the market price ________ and in the long run the number of firms ________ and the price is ________ the price was in the short run. A) rises; does not change; is equal to B) rises; increases; higher than C) rises; does not change; lower than D) falls; decreases; is equal to E) rises; increases; lower than
Sometimes economists disagree because their scientific judgments differ. Which of the following instances best reflects this source of disagreement?
a. One economist believes everyone should pay the same percentage of their income in taxes; another economist believes that wealthier citizens should pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes. b. One economist believes that manufacturing firms should face greater regulation to preserve the environment; another economist believes the government should not intervene in free markets. c. One economist believes that equality should be valued over efficiency in policy decisions; another economist believes that efficiency should be valued over equality in policy decisions. d. One economist believes the government should tax a household's income; another economist believes the government should tax a household's consumption.
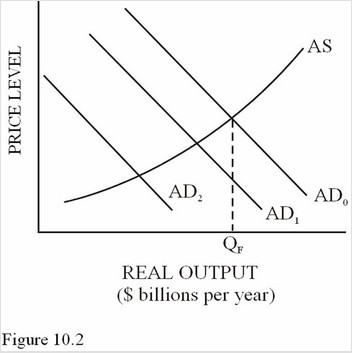 Suppose an initial increase in spending cause the aggregate demand curve in Figure 10.2 increases by a total of $60 billion, from AD2 to AD0. Equilibrium GDP will
Suppose an initial increase in spending cause the aggregate demand curve in Figure 10.2 increases by a total of $60 billion, from AD2 to AD0. Equilibrium GDP will
A. Increase by less than $60 billion because some of the additional spending drives up prices. B. Increase by $60 billion. C. Decrease because higher inflation causes unemployment. D. Increase by more than $60 billion because of the multiplier effect.