Cells in cartilage that produce ground substance are called ________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
chondroblasts/chondrocytes
You might also like to view...
Bacteria do not have organelles. How are they able to carry out photosynthesis?
A) They are parasites of plants that do have organelles. B) They interact in a symbiotic relationship with eukaryotic plants. C) They use their cell membrane to carry out photosynthesis. D) DNA in the nucleoid captures solar energy. E) 70S ribosomes function as photosystems.
The gametophyte generation of plants begins ____, where meiosis produces ____
a. after fertilization; a multicellular, diploid organism b. after fertilization; a multicellular; haploid organism c. in the sporangia; a multicellular; diploid organism d. in the sporangia; haploid spores e. in the sporangia; diploid spores
The following graph represents the concentration of cyclins over the course of the cell cycle. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the phase of the cell cycle where the blue arrow is pointing?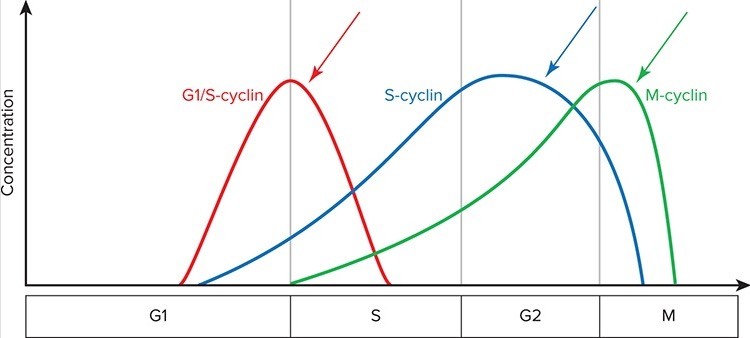 McGraw-Hill Education
McGraw-Hill Education
A. At this point in the cycle the cell is determining if environmental conditions are favorable for growth and proliferation. B. At this point in the cell cycle, DNA has already been replicated and divided into two daughter nuclei. C. At this point in the cell cycle, chromosomes have properly aligned on the metaphase plate and are beginning to separate. D. At this point in the cycle the cell is continuing to grow and make abundant tubulin proteins. E. At this point in the cell cycle, the cell has determined that the DNA is intact, that environmental conditions are favorable, and it is preparing for DNA replication.
A stem cell divides into two daughter cells. One of the daughter cells goes on to become a terminally differentiated cell. What is the typical fate of the other daughter cell?
What will be an ideal response?