Private goods are
A. rival in consumption, and their benefits are nonexcludable.
B. rival in consumption, and their benefits are excludable.
C. nonrival in consumption, and their benefits are nonexcludable.
D. nonrival in consumption, and their benefits are excludable.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
When a competitive price-taker market is in long-run equilibrium
a. the firms in the market will earn zero economic profit. b. the average total cost of the firms in the market will be minimized. c. every unit of the relevant good that is valued more than its opportunity costs will be produced and sold. d. all of the above are correct.
Given the graph, the quantity that would be associated with the price of $1 in a demand table would be: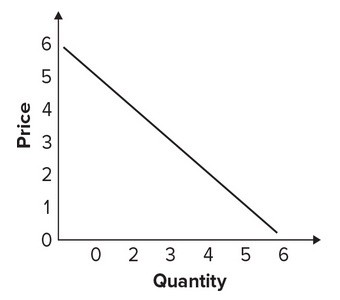
A. 6. B. 5. C. 4. D. 3.
If the demand for a monopolist's product increases, its
A) marginal revenue increases, making it more profitable to hire more workers. B) marginal revenue increases, making it more profitable to hire fewer workers. C) marginal revenue decreases, making it more profitable to hire more workers. D) marginal revenue decreases, making it more profitable to hire fewer workers.
The other name for the National Labor Relations Act of 1935 is
A) the Wagner Act. B) the Taft-Hartley Act. C) the Clayton Act. D) the Wheeler-Lea Act.