The rate at which a consumer is willing to trade one good for another to maintain the same level of satisfaction is affected by the
a. prices of the products.
b. amount of each good the consumer is currently consuming.
c. consumer's income.
d. marginal value product.
b
You might also like to view...
Use the figure below to answer the next question. 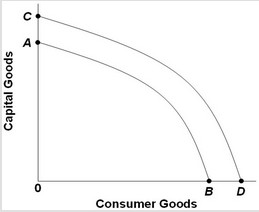 An increase in an economy's labor productivity would
An increase in an economy's labor productivity would
A. shift the production possibilities frontier from CD to AB. B. move the economy away from point B and toward point A. C. shift the production possibilities frontier from AB to CD. D. move the economy away from point A and toward point B.
Consider the following statement: "If the government attempts to raise employment through increased fiscal spending, all it will end up doing is increasing the price level." The statement rests on the assumption that:
a. the aggregate demand curve is a horizontal line. b. the aggregate supply curve is a vertical line. c. the aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping. d. the aggregate supply curve is downward-sloping. e. the aggregate supply curve is a horizontal line.
One problem for economic stability is that in a period of inflation
a. banks will be tempted to increase lending in order to increase profits. b. banks will be tempted to decrease lending in order to increase profits. c. profit-oriented banks will tend to hold excess reserves and decrease the money supply. d. deposits will decrease and banks will have to reduce lending.
The temptation of imperfectly-monitored workers to shirk their responsibilities is
a. an example of the moral hazard problem. b. an example of the adverse selection problem. c. an example of screening. d. an example of signaling.