A container of ideal gas at STP undergoes an isothermal expansion and its entropy changes by 3.7 J/K. How much work does it do?
A. zero
B. 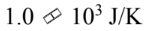
C. 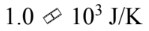
D. none of the above.
B. 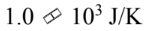
You might also like to view...
Why aren't small asteroids spherical in shape?
A) Small asteroids have odd shapes because they were all chipped off larger objects. B) Large asteroids became spherical because many small collisions chipped off pieces until only a sphere was left; this did not occur with small asteroids. C) The strength of gravity on small asteroids is less than the strength of the rock. D) Large asteroids were once molten and therefore became spherical, but small asteroids were never molten.
At the surface of Saturn's atmosphere the strength of the magnetic field is
A) about the same as Mercury's magnetic field at its surface. B) about the same as Venus' magnetic field at its surface. C) about the same as Earth's magnetic field at its surface. D) about the same as Mars' magnetic field at its surface. E) about the same as Jupiter's magnetic field at its atmospheric surface.
The electric flux through the two adjacent spherical surfaces shown below is known to be the same
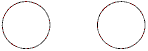
It is also known that there is no charge inside either spherical surface. We can conclude that
a.
there is no electric field present in this region of space.
b.
there is a constant E field present in this region of space.
c.
the electric flux has a constant value of zero.
d.
any of the above may be correct.
e.
only (a) and (b) above may be correct.
Consider the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom. (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s)
(a) How much energy (in eV) is needed to cause a transition of an electron from the second excited state to the third excited state? (b) What wavelength photon just has enough energy to initiate the transition in (a)?