If a = 3.0 mm, b = 4.0 mm, Q1 = 60 nC, Q2 = 80 nC, and q = 32 nC in the figure, what is the magnitude of the electric force on q?
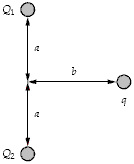
a.
1.6 N
b.
1.3 N
c.
1.9 N
d.
2.2 N
e.
0.040 N
b
You might also like to view...
A block of mass m sits at rest on a rough inclined ramp that makes an angle ? with the horizontal. What must be true about force of static friction f on the block?
A) f = mg sin ? B) f = mg cos ? C) f > mg D) f > mg cos ? E) f > mg sin ?
A free electron and a free proton are released in identical electric fields. (i) How do the magnitudes of the electric force exerted on the two particles compare?
1.It is millions of times greater for the electron. 2.It is thousands of times greater for the electron. 3.They are equal. 4.It is thousands of times smaller for the electron. 5.It is millions of times smaller for the electron.
A rock is suspended from a scale reads 20.0 N. A beaker of water (having a density of 1000 kg/m3) is raised up so the rock is totally submerged in the water. The scale now reads 12.5 N. What is the density of the rock?
A) 1.60 × 103 kg/m3 B) 2.50 × 103 kg/m3 C) 2.33 × 103 kg/m3 D) 3.00 × 103 kg/m3 E) 2.67 × 103 kg/m3
All three circuits below have R = 100 ?, C = 1.0 mF, and emf ? = (5.0 V) sin (377 t). The inductors in (B) and (C) are placed sufficiently far apart so that they do not alter one another's inductance. Such inductors add combine like resistors. Which statement regarding the angular resonance frequencies ?A, ?B, and ?C is correct?
?
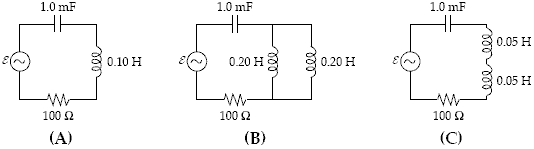
A. ?C>?A = ?B B. ?C