X-rays with a wavelength of 0.00100 nm are scattered at 130° by free electrons
What is the kinetic energy of each recoil electron? (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s)
A) 0.68 MeV B) 0.34 MeV C) 0.99 MeV D) 2.0 MeV E) 0.50 MeV
C
You might also like to view...
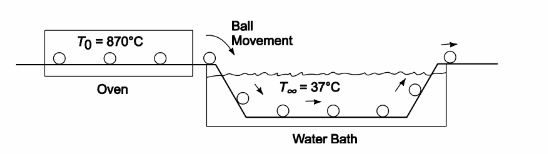
Ball bearings are to be hardened by quenching them in a water bath at a temperature of 37°C. You are asked to devise a continuous process in which the balls roll from a soaking oven at a uniform temperature of 870°C into the water, where they are carried away by a rubber conveyer belt. The rubber conveyor belt, however, is not satisfactory if the surface temperature of the balls leaving the water is above 90°C. If the surface coefficient of heat transfer between the balls and the water may be assumed to be equal to 590 W/(m2 K), (a) find an approximate relation giving the minimum allowable cooling time in the water as a function of the ball radius for balls up to 1.0-cm in diameter, (b) calculate the cooling time, in seconds, required for a ball having a 2.5- cm-diameter, and (c)
calculate the total amount of heat in watts which has to be removed from the water bath in order to maintain a uniform temperature if 100,000 balls of 2.5-cm-diameter are to be quenched per hour.
GIVEN

FIND
(a) An approximate relation giving the minimum allowable cooling time in the water as a function of the ball
radius for balls upto 1.0 cm in diameter
(b) The cooling time, in seconds, required for a ball having a 2.5-cm-diameter
(c) The total amount of heat in watts which would have to be removed from the water bath in order to
maintain its temperature uniform if 100,000 balls of 2.5 cm diameter are to be quenched per hour
ASSUMPTIONS
The ball bearings are 1% carbon steel
SKETCH
Suppose we subject a golf ball and a more massive lead ball to identical net forces. Then, compared to the golf ball, the lead ball must have
A) a larger acceleration. B) a larger speed. C) a smaller speed. D) a smaller acceleration. E) None of the above answers is necessarily true.
Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: A 60-kg skier starts from rest from the top of a 50-m high slope. If the work done by friction is -6.0 kJ, what is the speed of the skier on reaching the bottom of the slope?
A. 17 m/s B. 24 m/s C. 28 m/s D. 31 m/s
Why will a smaller body (the Moon, for example) cool much faster than a larger body like Earth?
A. A smaller body will have a smaller iron core, which holds heat better than rock. B. A smaller body has a larger surface area for heat to escape through, relative to its volume. C. A smaller body will have a smaller proportion of radioactive elements. D. A smaller body is less likely to have an atmosphere than a larger body.