Under a cap-and-trade program, what would happen if governments reduce firms' pollution caps?
A. The marketing cleaning price of pollution permits will not change.
B. The market clearing price of pollution permits will increase.
C. The marketing clearing price of pollution permits will cease to exist.
D. The market cleaning price of pollution permits will decrease.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A country has an absolute advantage in the production of a good if that country
a. can produce the good using fewer resources than another country would require b. has the lowest opportunity cost of producing the good and can produce it with the fewest resources c. has the lowest opportunity cost of producing the good regardless of whether it is produced with the fewest resources d. has the greatest opportunity cost of producing the good regardless of whether it is produced with the fewest resources e. has the greatest opportunity cost of producing the good and produces it with the fewest resources
Which of the following correctly describes the trend in the percentage of U.S. families living in poverty?
a. The poverty rate has steadily increased from approximately 5 percent in 1960 to over 40 percent in 1997. b. The poverty rate has steadily declined from approximately 40 percent in 1960 to under 5 percent today. c. The poverty rate steadily declined from about 22 percent in 1959 to about 12 percent in 1969, and has fluctuated since then. The poverty rate in 2002 was approximately 12.1 percent. d. The poverty rate steadily increased from about 12 percent in 1960 to about 22 percent in 1970, and has fluctuated since then.
What are the four main limitations of GDP accuracy?
(D) Depreciation, price level, distortion, and underground economy. (B) Nonmarket activities, underground economy, negative externalities, and quality of life. (C) Durable good, nondurable good, black market, and negative externalities. (D) Trough, peak, recession, and depression.
Refer to the information provided in Table 24.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 24.2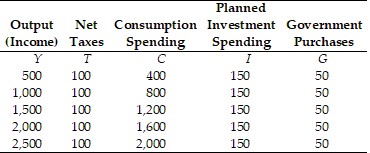 Refer to Table 24.2. At an output level of $1,500, disposable income
Refer to Table 24.2. At an output level of $1,500, disposable income
A. is $1,000. B. is $1,200. C. is $1,400. D. cannot be determined from this information.