A country currently is using all its land to produce wheat and grapes. However, the land most suited to growing grapes is being used to produce wheat, and the land most suited to growing wheat is being used to produce grapes. This is an example of
a. increasing opportunity costs
b. involuntary unemployment
c. productive inefficiency
d. central planning
e. communal ownership
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the scenario above. If the population of the economy is 200, the per capita national income is:
A) $17. B) $50. C) $10. D) $35.
Allocative efficiency occurs when
A) we cannot produce more of any good without giving up some other good that we value more highly. B) we cannot produce more of any one good without giving up some other good. C) marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost. D) opportunity costs are decreasing.
The rental rate approach to investment choices by firms and the present value approach
a. always agree. b. agree only if depreciation is 0. c. agree only if the price of equipment does not change. d. agree only when inflation rates are zero.
Refer to Figure 9.4. The payoffs to each firm (in billions of dollars) and an extensive form game between BP and Shell are shown in the figure. BP has 20 percent of the U.S. gasoline market share and Shell has 16 percent market share. BP and Shell are attempting to determine whether to send geologists to explore Oil Track 20.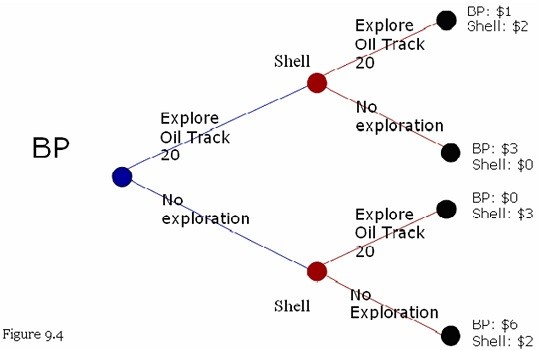 (a) Is there a dominant strategy for Shell? What is the dominant strategy, if any, for Shell?(b) What is the Nash equilibrium or equilibria in this game?(c) What is a first-mover advantage? Does BP have a first-mover advantage in this game?(d) Use the above information to advise BP on whether they should pursue a merger with Shell.
(a) Is there a dominant strategy for Shell? What is the dominant strategy, if any, for Shell?(b) What is the Nash equilibrium or equilibria in this game?(c) What is a first-mover advantage? Does BP have a first-mover advantage in this game?(d) Use the above information to advise BP on whether they should pursue a merger with Shell.
What will be an ideal response?